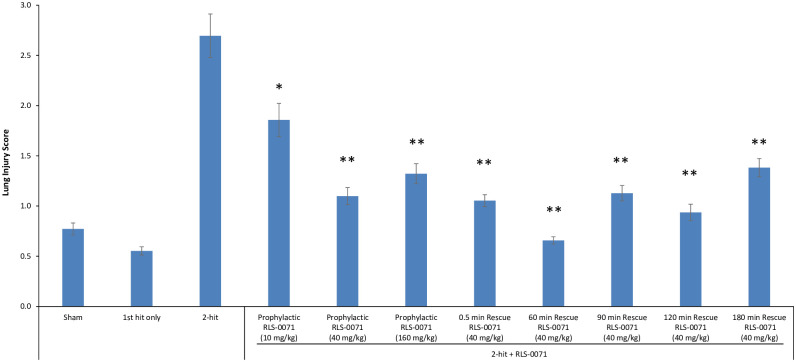
Fig 3. Prophylactic or rescue dosing of RLS-0071 reduces neutrophil-mediated lung injury.
H&E stained lung tissue images were converted to black and white and quantified by ImageJ analysis. The ratio of black to white pixels was calculated and used as a measure of lung injury (Y axis). Sham control animals (n = 3), first hit only (n = 2), 2-hit (n = 3), 2-hit + 10 mg/kg prophylactic dose RLS-0071 (n = 4), 2-hit + 40 mg/kg prophylactic dose RLS-0071 (n = 6), 2-hit + 160 mg/kg prophylactic dose RLS-0071 (n = 9), 2-hit + 40 mg/kg rescue dose RLS-0071 at 0.5 min (n = 4), 2-hit + 40 mg/kg rescue dose RLS-0071 at 60 min (n = 3), 2-hit + 40 mg/kg rescue dose RLS-0071 at 90 min (n = 5), 2-hit + 40 mg/kg rescue dose RLS-0071 at 120 min (n = 3) and 2-hit + 40 mg/kg rescue dose RLS-0071 at 180 min (n = 3). Ten images or more were quantified per slide for each animal. Data are means and standard error of the means. Statistical analysis was performed using a Generalized Linear Model. * denotes p = 0.002 and ** denotes p<0.001 compared to 2-hit animals.