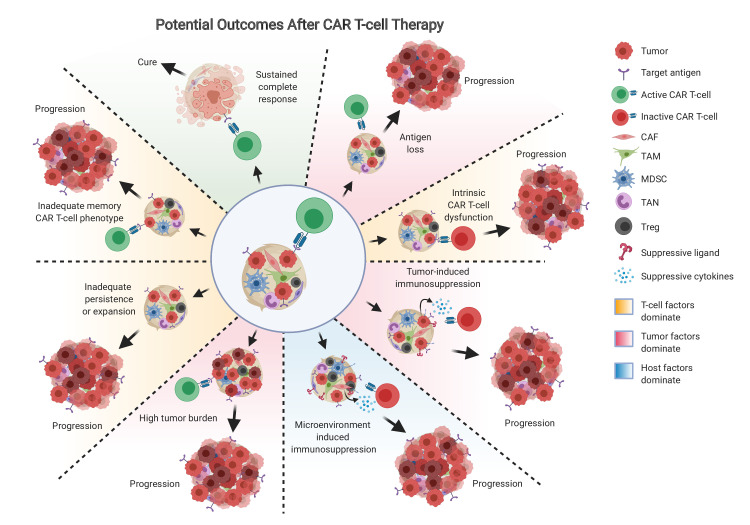
Figure 2.
Potential outcomes after CAR T-cells. Cancer may progress or relapse after CAR T-cells due to tumor-related factors (red background), such as antigen escape, tumor-induced immunosuppression such as PD-L1 or suppressive cytokine production, or high tumor burden relative to functional CAR T-cells; T-cell factors may dominate (orange background), such as intrinsic CAR T-cell dysfunction, inadequate persistence or expansion of the CAR T-cells in vivo, or inadequate memory phenotype achieved by the CAR T-cells; host factors (blue background) may impel resistance to CAR T-cells, such as microenvironment-induced immunosuppression driven by CAF, TAM, MDSC, TAN, or Treg. CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; MDSCs, marrow-derived suppressor cells; TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; TAN, tumor-associated neutrophils; Tregs, regulatory T cells.