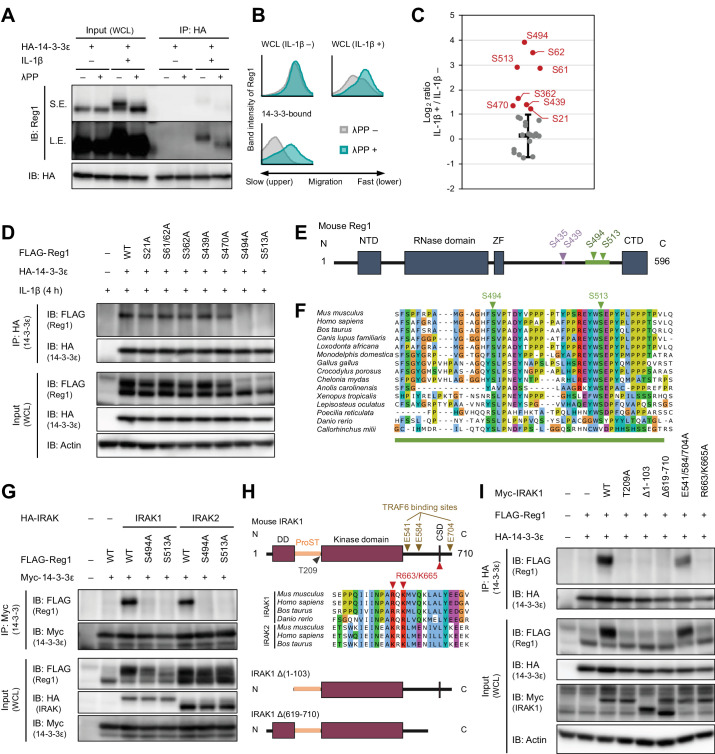
Figure 2. IL-1β-induced phosphorylation of Regnase-1 at S494 and S513 is necessary for Regnase-1-14-3-3 binding.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of λPP-treated immunoprecipitates (IP: HA) and WCL from HeLa cells transiently expressing HA-14-3-3ε stimulated with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 4 hr. S.E.: short exposure, L.E.: long exposure. (B) The intensity of Regnase-1-bands in (A). (C) Quantitation of phosphosites on Regnase-1 in HeLa cells stimulated with or without IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 4 hr. Each dot shows phosphosite quantitative ratio between IL-1β + and IL-1β -. Phosphosites with log2 ratio > one were colored with red. Black horizontal line shows Regnase-1 protein quantitative ratio derived from the average of non-phosphopeptide quantitative ratios, and its error bars show the standard deviation. (D) Immunoblot analysis of immunoprecipitates (IP: HA) and WCL from HeLa cells transiently expressing HA-14-3-3ε and FLAG-Regnase-1-WT or indicated mutants stimulated with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 4 hr. (E) Schematic illustration of Regnase-1 protein. The amino acid sequence including S494 and S513 shown in (F) is highlighted in green. NTD: N-terminal domain, ZF: Zinc finger domain, CTD: C-terminal domain. (F) The amino acid sequences including S494 and S513 of Regnase-1 from mouse and other indicated vertebrates. (G) Immunoblot analysis of immunoprecipitates (IP: Myc) and WCL from HeLa cells transiently expressing Myc-14-3-3ε, HA-IRAK1/2, and FLAG-Regnase-1-WT or indicated mutants. (H) Schematic illustration of IRAK1 protein. The amino acid sequence in CSD of IRAK1 and IRAK2 from mouse and other indicated vertebrates are also shown. DD: Death domain, CSD: C-terminal structural domain. (I) Immunoblot analysis of immunoprecipitates (IP: HA) and WCL from HeLa cells transiently expressing FLAG-Regnase-1-WT, HA-14-3-3ε, and Myc-IRAK1-WT or indicated mutants.
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Regnase-1 bands migrate slower in LPS-stimulated samples.
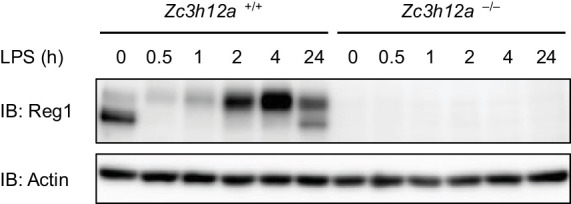
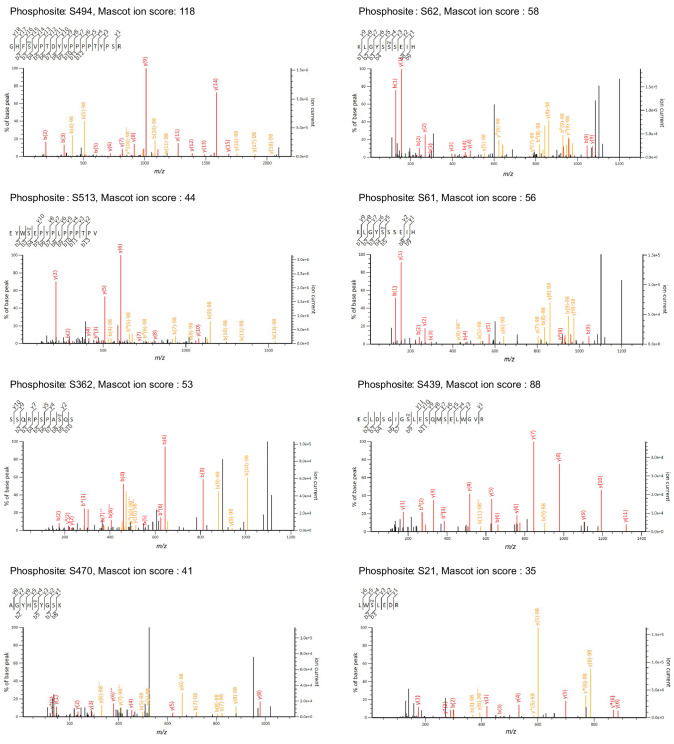
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Candidate spectra of Regnase-1 phosphopeptides with confident site localization.
Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Regnase-1-14-3-3 interaction is impaired in IRAK1/2-depleted cells.
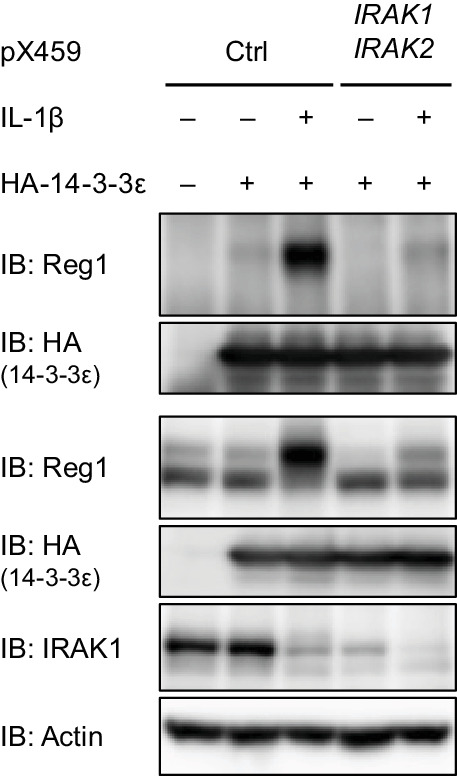
Figure 2—figure supplement 4. Schematic illustration of IRAK1.
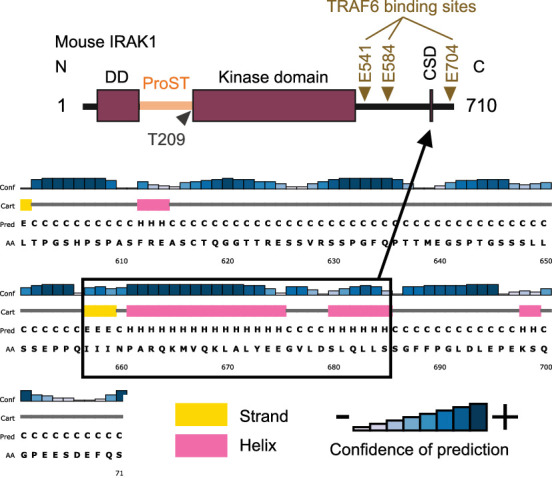
Figure 2—figure supplement 5. R663/K665A mutation does not abrogate IRAK1-mediated NF-κB activation.
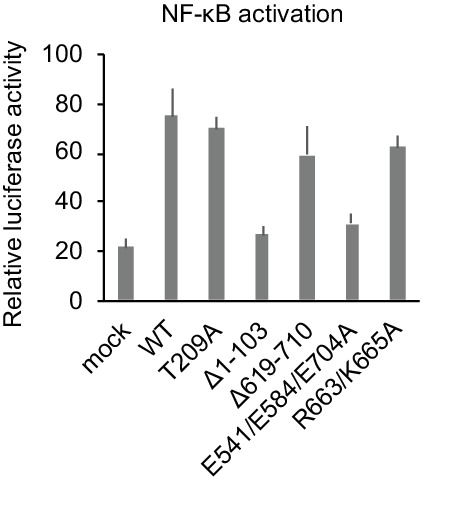
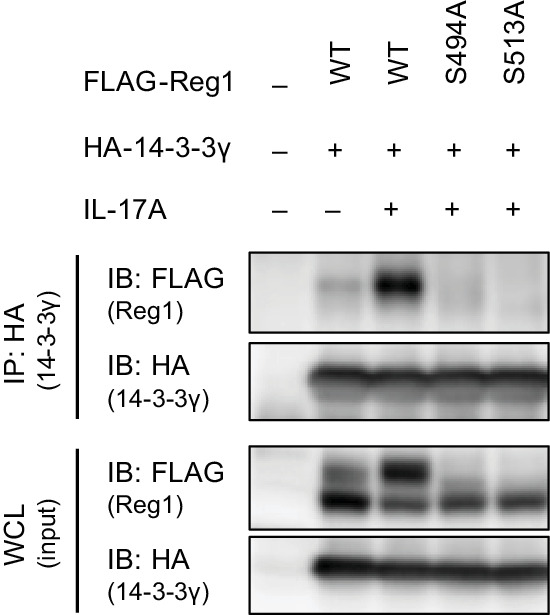
Figure 2—figure supplement 6. IL-17A stimulation induces phosphorylation at S494 and S513 of Regnase-1.
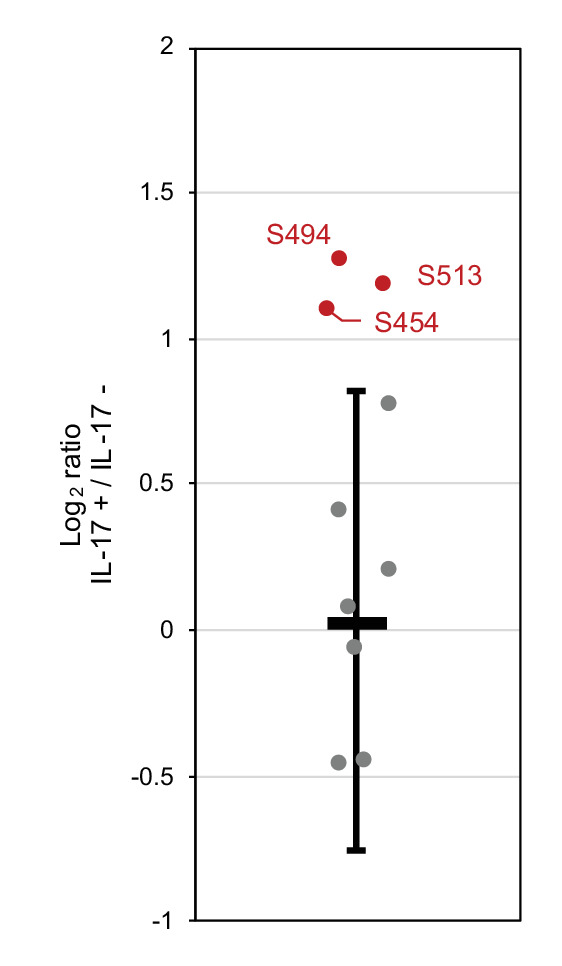
Figure 2—figure supplement 7. Candidate spectra of Regnase-1 phosphopeptides with confident site localization.
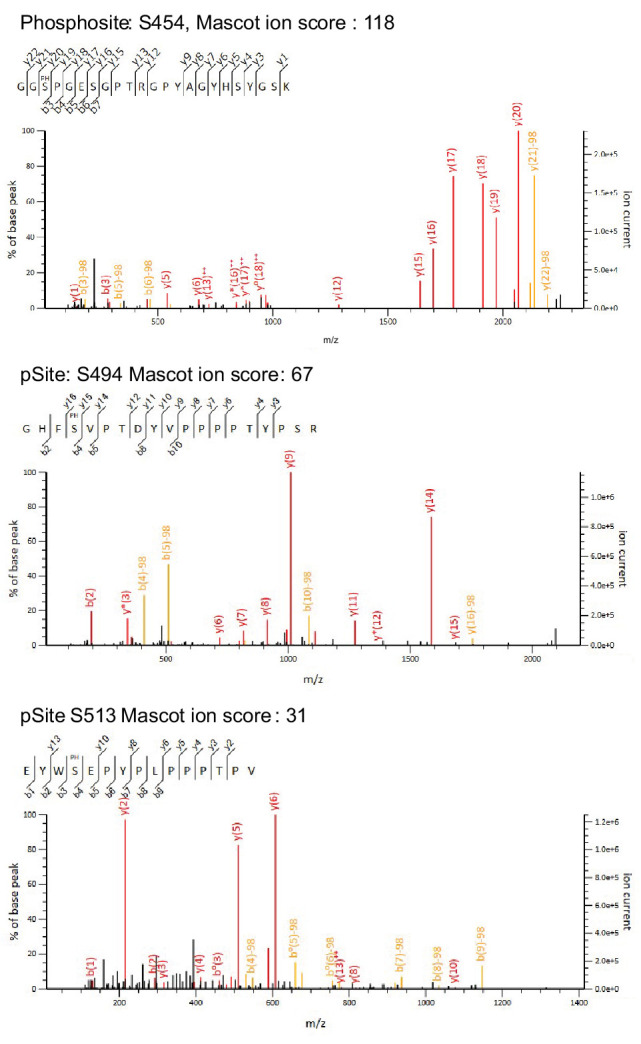
Figure 2—figure supplement 8. IL-17A stimulation induces Regnase-1-14-3-3 association.