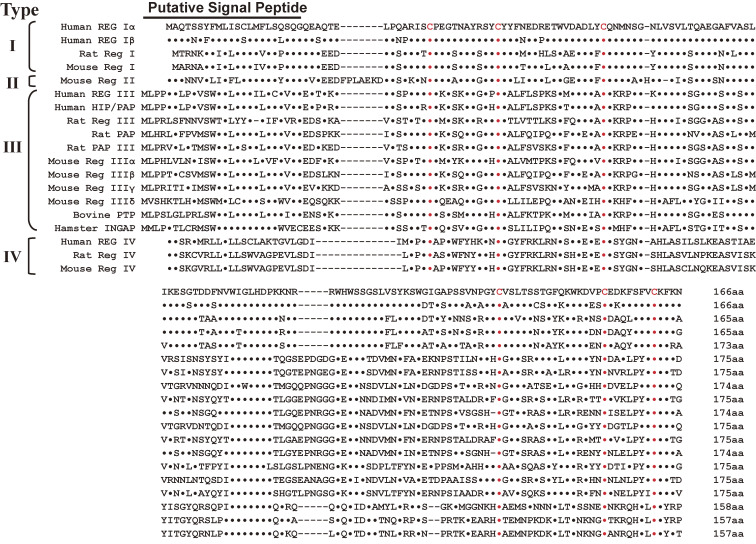
Figure 18.
Alignment of amino acid sequences of the Reg gene family. Based on the primary structures of the encoded proteins (adapted from Refs. 96, 195 and 293), the members of the Reg gene family are grouped into four subclasses, types I, II, III and IV. Dots indicate amino acids identical to human REG Iα. Dashes indicate gaps for maximal alignment. Six conserved cysteines in the mature proteins are indicated by red. Type I, II, and III Reg genes are clustered in a restricted region of the same chromosome.195,196,198,293) Human REG-related sequence (RS) is omitted from the alignment because human RS is a pseudogene.168) Recently, hamster Reg IIIβ (XM_021231969.2), Reg IIIγ (NM_001281579.1) and Reg IV (XM_021235470.2), shrew Reg IIIα (XM_006169192.2), Reg IIIγ (XM_006169191.2) and Reg IV (XM_006166291.1), rabbit Reg IIIγ (XM_002709697.2) and Reg IV (XM_002715670.3), canine Reg IIIα (NM_001002945.3) and Reg IV (XM_038626000.1), guinea pig Reg IIIβ (XM_003468964.1) and Reg IIIγ (XM_003468904.4), bovine Reg IV (NM_001076986.1), porcine Reg IIIγ (XM_005662419.3) and Reg IV (NM_001190251.1), equine Reg IIIγ (XM_001498171.6), ferine Reg IV (XM_023259045.1), kangaroo Reg IIIβ (XM_013031828.1), suncus Reg IIIα (LC606672), bat Reg IIIα (XM_033125205.1), Reg IIIγ (XM_024558600.1) and Reg IV (XM_024570607.1), chicken Reg IV (NM_001277527.1), quail Reg IV (XM_015869386.1), and frog Reg Iβ (XM_002934582.4) and Reg IV (XM_004915988.3) were isolated. The 6 cysteines are completely conserved among the spices in the primary structure.