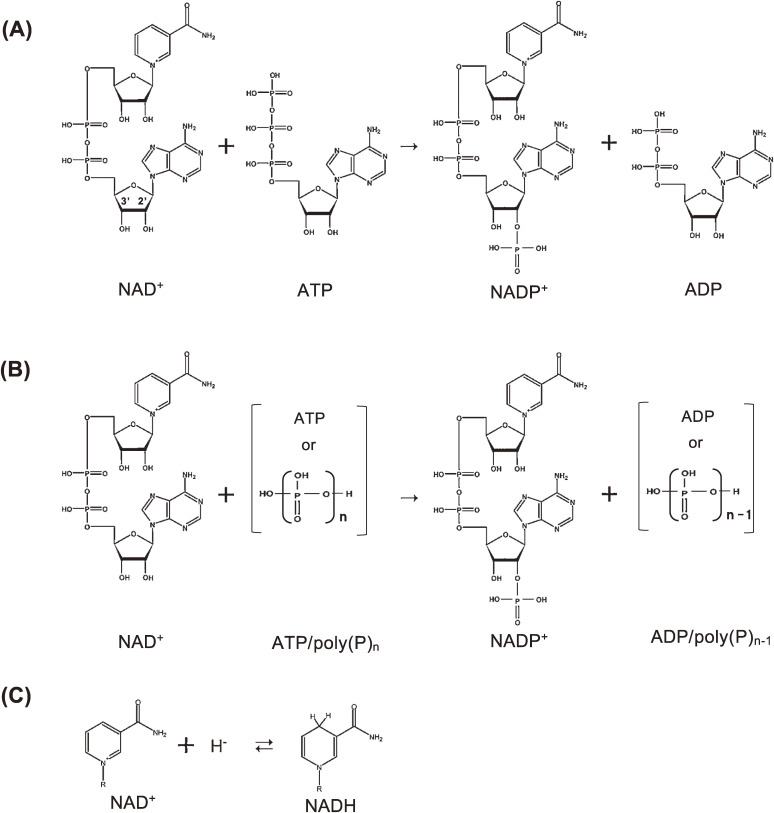
Figure 1.
NAD kinase reactions. (A) ATP-NAD kinase reaction. NAD+ is phosphorylated to NADP+ by using only ATP. (B) ATP/poly(P)-NAD kinase reaction. NAD+ is phosphorylated to NADP+ by using ATP or poly(P). Linear and cyclic poly(P)s are then utilized. (C) Structures of NAD+ and NADH. A hydride ion (H−) is added to a nicotinamide moiety of NAD+, resulting in NADH. This figure was reproduced from S. Kawai and K. Murata (2008) Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 72, 919–930 (Ref. 63) with some modifications.