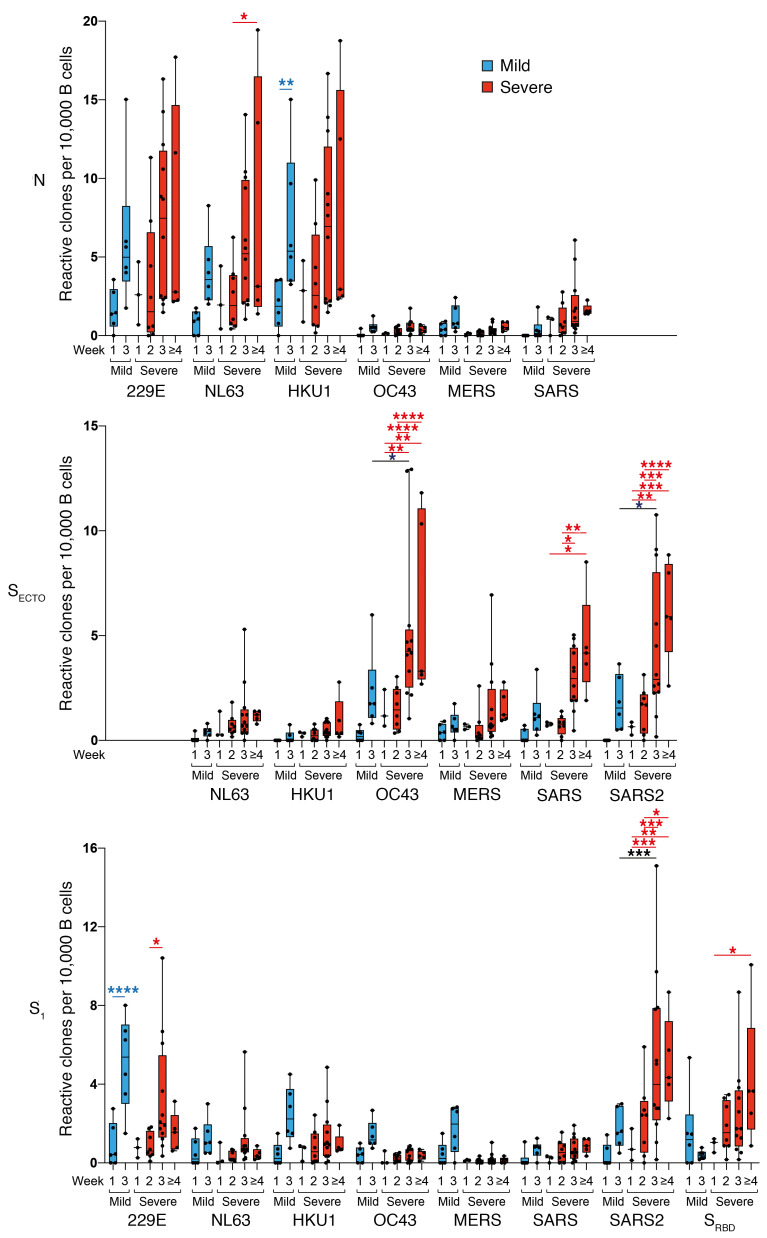
Figure 2. Patients with severe COVID-19 exhibit a prominent expansion of SARS-CoV-2 and OC43-SECTO–specific IgG B cells.
Normalized enumeration of in vitro–stimulated peripheral blood–derived IgG B cells from patients with mild COVID-19 (blue boxes) and patients with severe COVID-19 (red boxes) with reactivity to N, SECTO, and S1 coronavirus antigens and SARS-CoV-2 SRBD. Relative OC43-SECTO–, SARS-SECTO SARS2-SECTO/S1–, and SRBD-specific IgG B cell clones showed a highly significant outgrowth in the first 4 weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with severe COVID-19. In patients with mild COVID-19, a highly significant increase was only seen for 229E-S1–specific IgG clones 3 weeks after the onset of symptoms. Boxes represent the median, upper, and lower quartiles, and whiskers show the range. P values calculated using a 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001) are shown in black (intergroup significant differences), blue (significant mild COVID-19 intragroup differences), and red (severe COVID-19 intragroup significant differences).