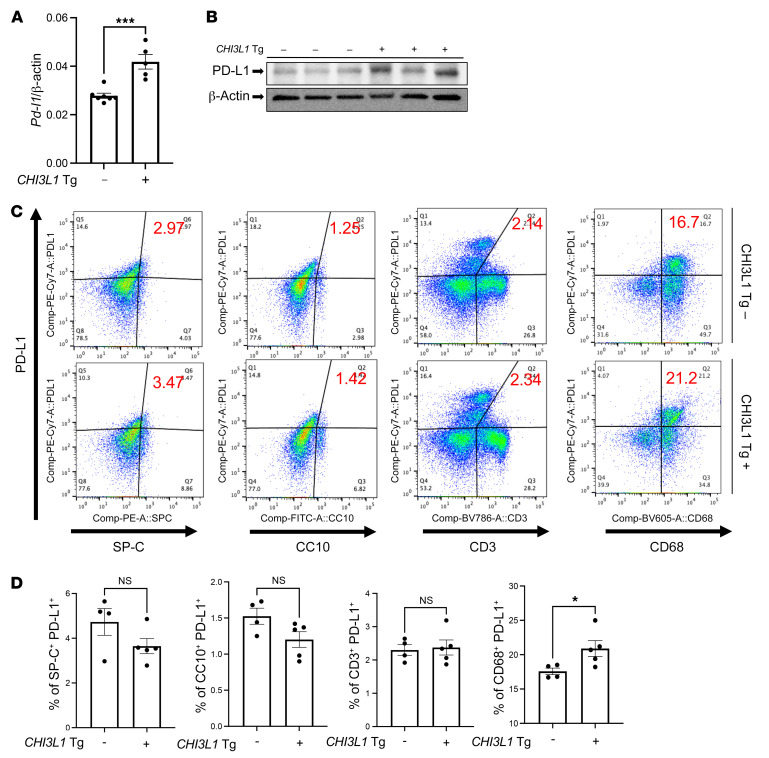
Figure 4. Transgenic CHI3L1 stimulates PD-L1 in the normal lung.
Eight-week-old WT (–) and CHI3L1-transgenic (+) mice were used to evaluate the expression and accumulation of PD-L1 in the lung. (A) RT-PCR was used to quantitate the levels of mRNA encoding PD-L1 in the lungs from WT mice (CHI3L1 Tg –) and mice in which CHI3L1 was overexpressed in the lung in a transgenic manner (CHI3L1 Tg +). Each dot represents the evaluation in an individual animal. (B) Western blot evaluations of PD-L1 accumulation in lungs from WT (CHI3L1 Tg –) and CHI3L1-transgenic (CHI3L1 Tg +) mice. (C and D) FACS evaluations quantitating the accumulation of PD-L1 in cell populations from lungs from WT and CHI3L1 Tg + mice. These evaluations used cell-specific markers of airway epithelial cells (CC10), alveolar epithelial cells (surfactant apoprotein C [SP-C]), dendritic cells (CD11c), and macrophages (F4/80). The values in A and D represent the mean ± SEM of the noted evaluations represented by the individual dots. B is representative of a minimum of 2 similar evaluations. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t test).