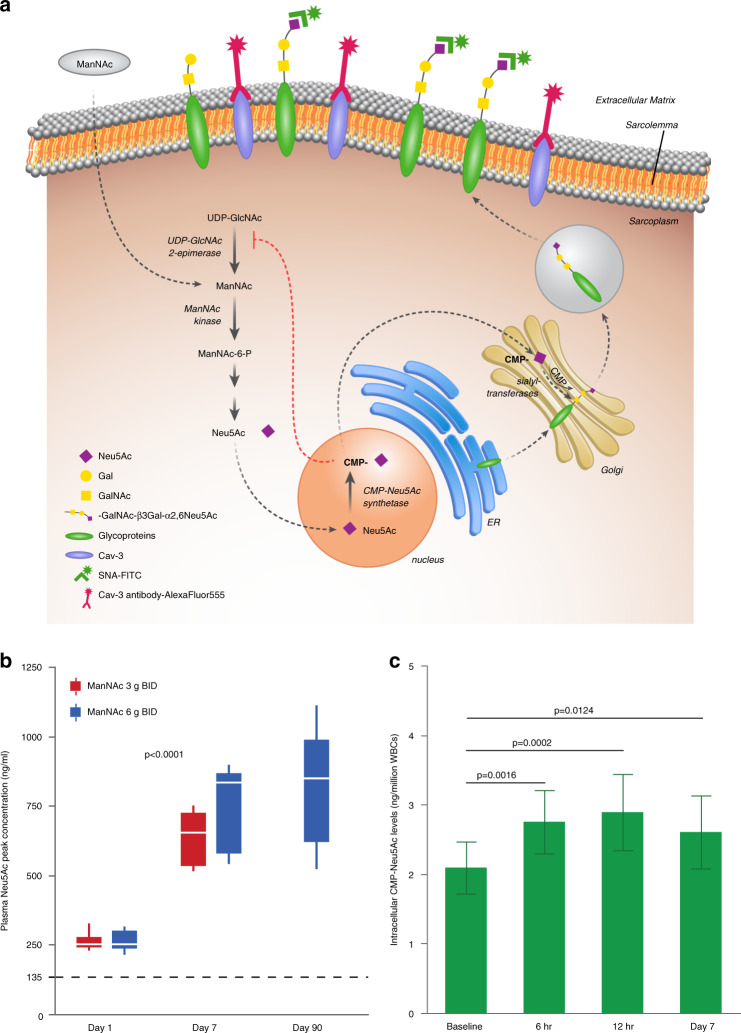
Fig. 2. Neu5Ac production.
(a) Decreased enzymatic activity of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) results in impaired Neu5Ac production and glycoprotein sialylation. The rate-limiting step in the pathway is catalyzed by UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase. ManNAc is phosphorylated by ManNAc kinase. Neu5Ac is activated in the cell nucleus to CMP-Neu5Ac, which acts as the donor of Neu5Ac in the reactions catalyzed by sialyltransferases to sialylate nascent glycoproteins in the Golgi. Sialylated glycoproteins are abundant on plasma membranes where they mediate several biological processes such as cellular adhesion, cell interactions, and signal transduction. FITC-labeled SNA lectin (green), which predominantly binds to terminal α2,6-linked Neu5Ac (Neu5Acα2,6Galβ), and antibodies against the sarcolemmal residence protein Caveolin-3 (Cav-3), are shown. Figure courtesy of Julia Fekecs. (b) Plasma peak concentrations of Neu5Ac by timepoint and dose. The dotted line denotes mean plasma concentration at baseline. To obtain SI units, multiply plasma Neu5Ac in ng/ml by 3.237 to obtain the concentration in nmol/L. (c) Intracellular CMP-Neu5Ac concentrations (mean, SD) measured by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS-MS) in white blood cells (WBCs) at baseline, 6 and 12 hours after initial dosing, and trough on day 7.