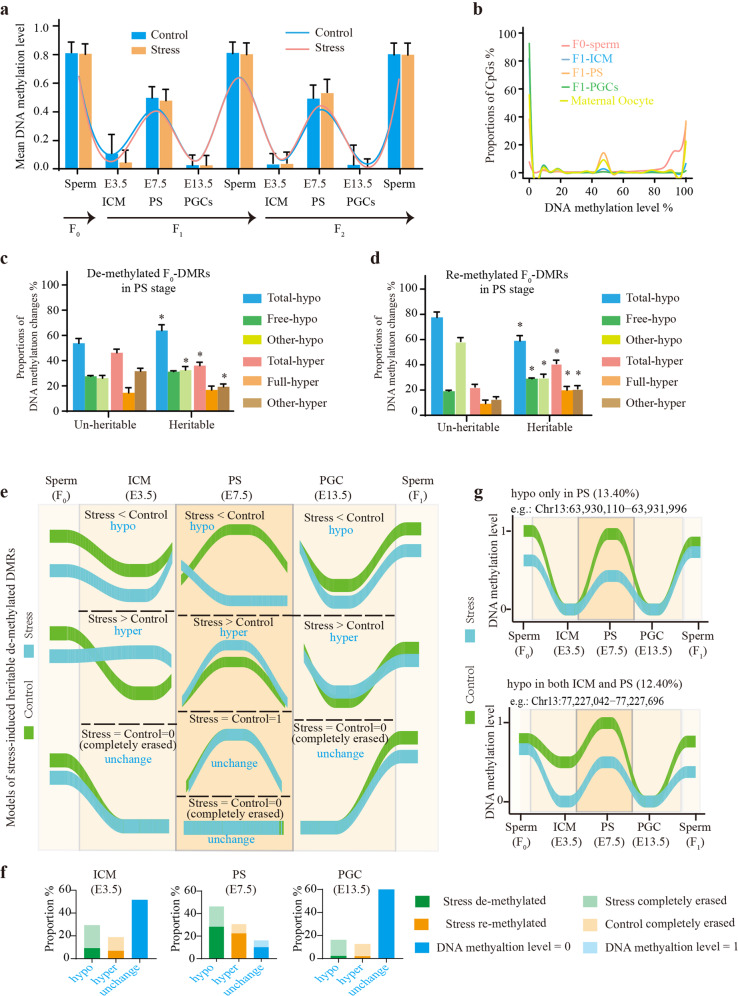
Fig. 5. Heritable DMRs have alterative DNA methylation reestablishment proportions and levels in the PS stage during embryonic reprogramming process.
a Mean DNA methylation levels in different embryo stages and sperm samples. b Distribution of the CpG dinucleotides in different DNA methylation levels. c Alterations in DNA methylation patterns of both the heritable and the un-heritable de-methylated F0-DMRs when compared with that of the paternal sperm samples during reprogramming process of the F1 generation. Total de-methylated (Total-hypo) events were composed of free-methylated (Free-hypo) events and the other de-methylated (Other-hypo) events, while total re-methylated (Total-hyper) events were composed of full-methylated (Full-hyper) events and the other re-methylated (Other-hyper) events. d Alterations in DNA methylation patterns of both the heritable and the un-heritable re-methylated F0-DMRs when compared with that of the paternal sperm samples during the reprogramming process of the F1 generation. e Dynamic DNA methylation patterns of the stress-induced heritable de-methylated DMRs during reprogramming process. In each stage, all DMRs were classified into three types: hypo (stress group was de-methylated), hyper (stress group was re-methylated), and unchanged (there was no difference between two groups). Theoretically, there were 36 combinations of the reprogramming patterns of these DMRs. f Proportion of each DMR type in each embryo stage. g The top two reprogramming patterns of the DMRs that were sequencing covered in all embryo samples of both the control and stress groups.