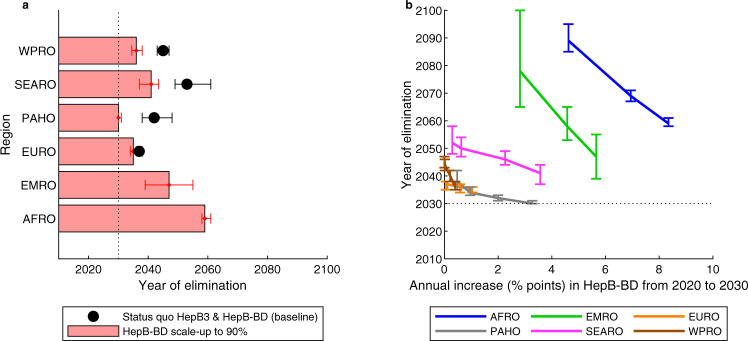
Fig. 4. The impact of timely HepB-BD scale-up on achieving WHO elimination targets.
a Median year by which the elimination target (0.1% HBsAg prevalence in five-year-olds) is reached in the WHO regions, with 95% credibility intervals, in the status quo HepB3 & HepB-BD scenario (black dots) and the scenario in which timely HepB-BD coverage is scaled up to ≥90% by 2030 (HepB-BD scale-up scenario; red bars). b Median year of elimination, with 95% credibility intervals, for different levels of annual scale-up of timely HepB-BD coverage (the HepB-BD scale-up scenarios) in the populations within each of the WHO regions. The dotted lines for the year 2030 are for reference purposes only. For each WHO region, number of HBsAg prevalent cases in five-year-olds and total number of five-year-olds were summed across countries. Number of HBsAg prevalent cases in five-year-olds was divided by total number of five-year-olds to give HBsAg prevalence in five-year-olds. The year of elimination was identified as the year in which HBsAg prevalence in five-year-olds falls below 0.1%. This was repeated n = 200 times using independent draws from the posterior distribution of each country. The six WHO regions AFRO, EMRO, EURO, PAHO, SEARO and WPRO are shown in Supplementary Fig. 1. HBsAg: hepatitis B surface antigen; HepB3: infant HBV vaccine series; timely HepB-BD: timely birth dose; WHO: World Health Organization.