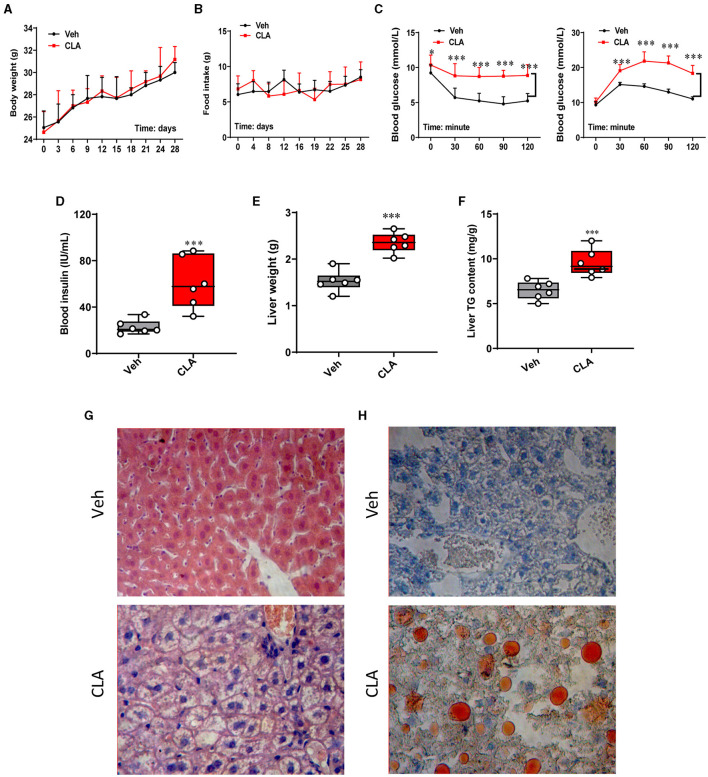
Figure 1.
Dietary CLA induces hepatic steatosis in mice. (A) Mice were fed either with a control diet/Vehicle or a diet with 1.5% (w/w) CLA supplementation for 28 days, during which the body weight and food intake (B) were measured. (C) Blood glucose (mmol L-1) following insulin or glucose tolerance test at 0, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min posterior to intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) injection of insulin. (D) Blood insulin (IU ml-1) levels were measured. (E) Liver weight (g) and (F) liver total triglycerides content (mg g−1). (G) Representative images of the liver sections stained with H&E. (H) Representative images of the liver sections stained with Oil Red O showing increased lipid deposition in CLA-treated mice. Duplicate slides per animal were analyzed. The data are shown as the means ± SEM, n = 6, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 using two-tailed student's t-test.