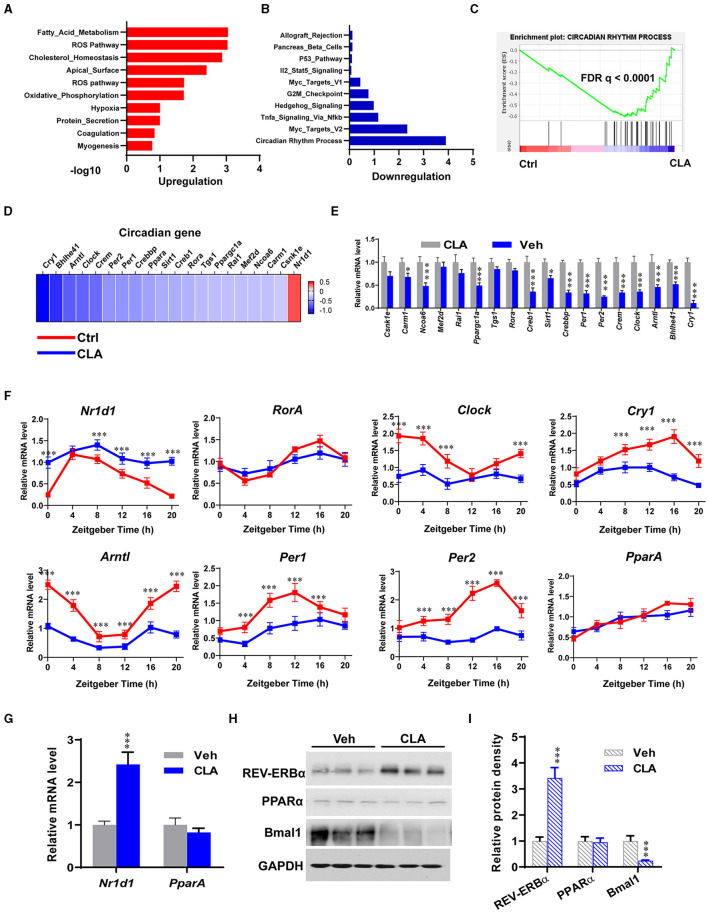
Figure 2.
Dietary CLA disrupts the circadian clock gene program in the liver. Gene ontology analysis of the upregulated (A) and downregulated (B) genes in the livers of CLA mice compared to that of the control groups. Hypergeometric test and Benjamini-Hochberg p-value correction was applied. (C) GSEA plots depicting the enrichment of genes downregulated in the circadian rhythm process of livers from CLA-treated mice compared to the controls. FDR, false-discovery rate. (D) Heatmap of mRNA expression (RNA-seq) changes of the circadian clock in the livers of CLA-treated mice (log2 transformed, normalized to Veh). (E) The qRT-PCR analysis confirmed changes of genes involved in the circadian clock in the livers. (F) Relative mRNA expression of canonical core clock genes in the livers. Livers were collected at each indicated ZT under a 12-h light/dark cycle. (G) Relative mRNA expression of transcription factors Nr1d1 encoding REV-ERBα and Pparα encoding PPARα, normalized to Gapdh expression. (H,I) Immunoblotting of REV-ERBα, PPARα, and Bmal1 protein expression normalized to GAPDH levels and quantification of relative protein density. The data are shown as the means ± SEM, n = 6 per group, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, using two-tailed student's t-test.