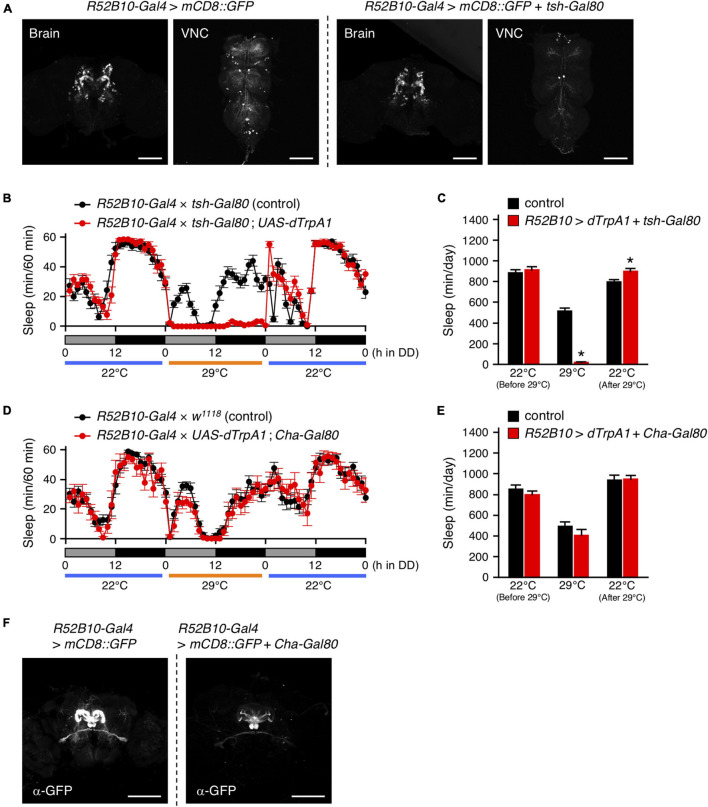
FIGURE 4.
Activation of R52B10-Gal4-expressing cholinergic neurons in the brain promotes wakefulness. (A) Maximum-intensity projection of the confocal brain or VNC images of flies expressing UAS-mCD8::GFP under the control of R52B10-Gal4 (left two panels) or R52B10-Gal4 with tsh-Gal80 (right two panels). The tsh-Gal80 efficiently suppressed R52B10-Gal4 driven GFP expression in the VNC, while did not in the brains. Scale bars represent 100 μm. (B,C) Sleep profiles in 60-min intervals (B) or total daily sleep (C) for control flies (R52B10-Gal4 × tsh-Gal80, black circles or bars, n = 16) or flies expressing dTrpA1 in R52B10-Gal4 brain neurons (R52B10-Gal4 × tsh-Gal80; UAS-dTrpA1, red circles or bars, n = 16) in DD. The behavior was monitored as described in Figure 2. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 vs. control; two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by simple main effect test. (D,E) Sleep profiles in 60-min intervals (D) or total daily sleep (E) for control flies (R52B10-Gal4 × w1118, black circles or bars, n = 16) or flies expressing dTrpA1 in R52B10-Gal4 except for cholinergic neurons (R52B10-Gal4 × UAS-dTrpA1; Cha-Gal80, red circles or bars, n = 7) in DD. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. (F) Maximum-intensity projection of the confocal brain images of flies expressing UAS-mCD8::GFP under the control of R52B10-Gal4 (left panel) or R52B10-Gal4 with Cha-Gal80 (right panel). Scale bars represent 100 μm.