Figure 1.
B cell response elicited by RBD-focused immunization included broadly cross-reactive cells
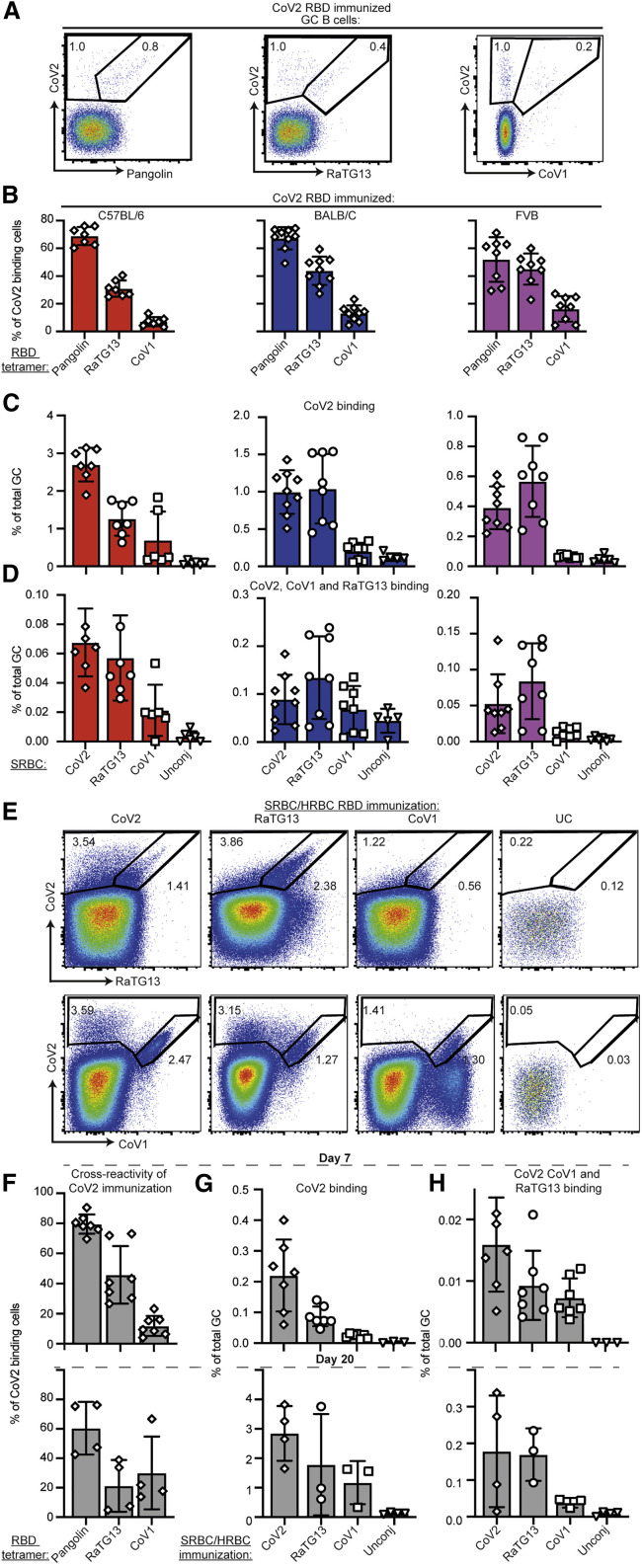
(A) Representative flow cytometric plots showing total GC B cells (TCRB–, CD11b–, B220+, Fas+, CD38–) simultaneously stained with four different fluorescent tetramers of the indicated sarbecovirus RBDs in the spleen of BALB/C mice 7 days following immunization with CoV2-RBD conjugated to SRBCs. Percentage of total CoV2-binding GC B cells and cross-reactive B cells are indicated on each plot.
(B) Percentage of CoV2 binding GC B cells also binding to the indicated sarbecovirus RBD tetramer in individual mice (symbols) and mean ± SEM from three different inbred strains.
(C and D) Percentage of all GC B cells binding the CoV2 RBD tetramer (C) or cross-reactively binding the CoV2, RaTG13, and CoV1 RBD tetramers (D) 7 days after immunization with the indicated RBD conjugated to SRBCs or unconjugated SRBCs as a negative control.
(E) Representative flow cytometric plots of GC B cells simultaneously stained with three different fluorescent tetramers of the indicated sarbecovirus RBDs in the spleen of Ig-humanized mice with a human antibody repertoire on day 20 following four immunizations with the indicated RBD conjugated first to SRBCs and then to HRBCs.
(F) Percentage of CoV2 binding GC B cells also binding the indicated sarbecovirus RBD tetramer in individual human antibody repertoire mice (symbols) after one immunization (day 7) or four immunizations (day 20) with CoV2 RBD.
(G and H) Percentage of all GC B cells binding the CoV2 RBD tetramer (G) or cross-reactively binding the CoV2, RaTG13, and CoV1 tetramers (H) in individual humanized antibody mice (symbols).
Data pooled from two independent experiments. Columns show mean ± SEM.
See also Figures S1–S3.