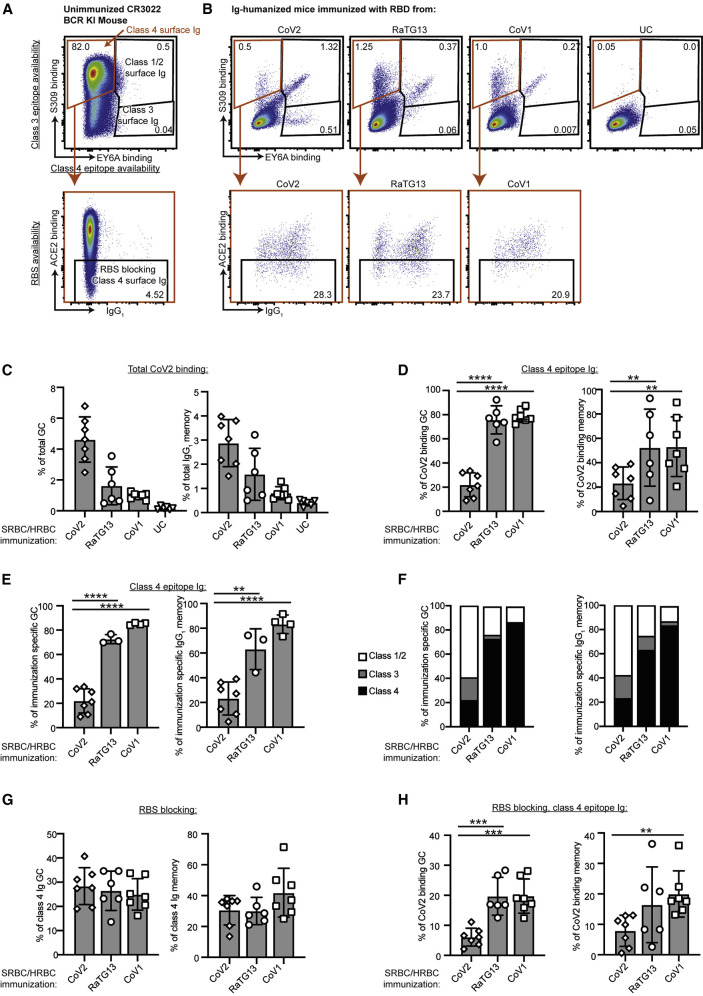
Figure 2.
Immunization with diverse RBDs shift epitope predominance of the B cell response
(A) Flow cytometric plot of spleen B cells in an unimmunized mouse with knocked in CR3022 V(D)J IGH and IGK exons encoding the prototypic class 4 epitope-specific membrane Ig, illustrating the strategy used to identify B cells recognizing different RBD epitopes based on competition for RBD binding between the membrane Ig on each cell and fluorescent ligands for class 4 (EY6A), class 3 (S309), and class 1/2 (ACE2) epitopes. B cells were first stained with CoV2 RBD, then with fluorescent anti-RBD antibodies S309 and EY6A, and finally with fluorescent ACE2.
(B) Representative flow cytometric plots of GC B cells in Ig-humanized mice on day 20 following immunization with the indicated RBDs coupled to SRBCs/HRBCs or unconjugated SRBCs/HRBCs (UC): (top panels) the proportion of B cells with membrane Ig-binding RBD and blocking either the class 4 (orange gate) or class 3 epitopes (S309– EY6A+) or class 1/2 epitopes (S309+ EY6A+); (bottom panels) the proportion of cells with membrane Ig binding the class 4 epitope but also precluding ACE2 binding.
(C) Percentage of total GC (B220+, Fas+, CD38–) B cells or IgG1 memory (B220+, IgG1+, Fas–) B cells binding to 200 ng/mL CoV2 RBD in individual Ig-humanized mice immunized with the indicated RBDs.
(D) Percentage of CoV2 RBD binding GC or IgG1 memory B cells binding to the class 4 epitope.
(E) Of GC or IgG1 memory B cells that bind the same RBD as was used for immunization, percentage that bind the class 4 epitope.
(F) Percentage of CoV2, CoV1, or RaTG13 binding GC or IgG1 memory B cells elicited by the indicated immunogens that bind to each of the indicated epitopes.
(G) Percentage of B cells with class 4 epitope binding Ig that precludes ACE2 binding.
(H) Percentage of CoV2 binding GC or IgG1 memory B cells binding to the class 4 epitope and blocking the RBS.
Data points represent individual mice. Columns show mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Data pooled from two independent experiments.