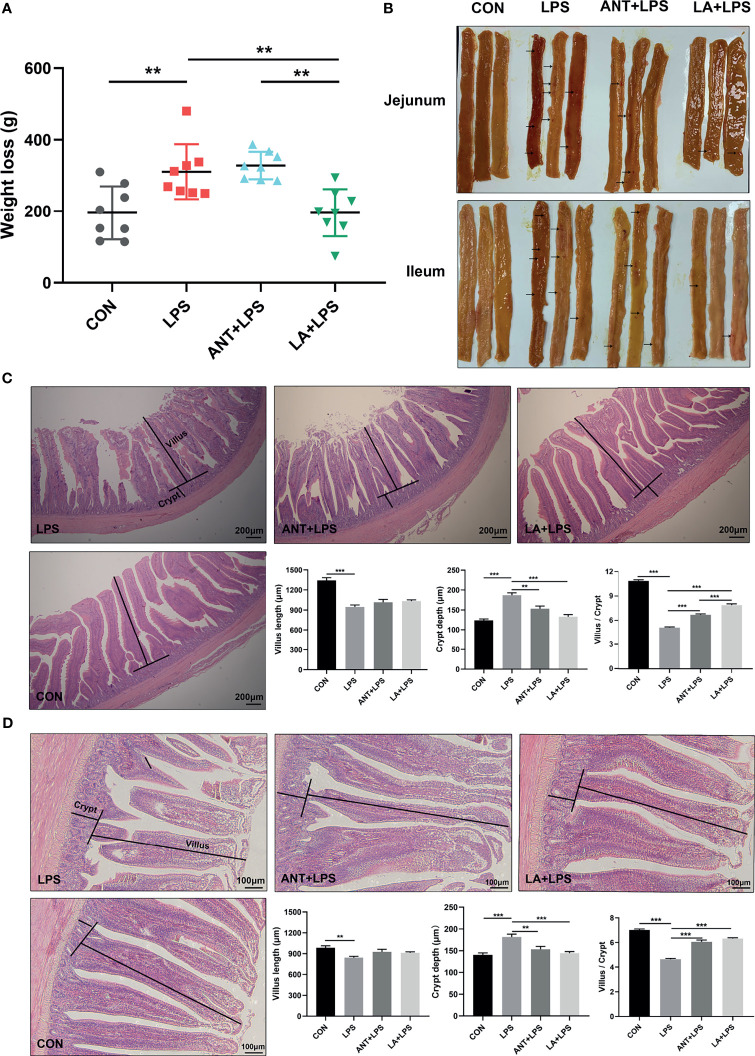
Figure 1.
Lauric acid (LA) attenuated the weight loss and intestinal injuries of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- challenged broilers. CON: fed with a basal diet and injected with saline; LPS: fed with a basal diet and injected with 0.5 mg/kg LPS; ANT+LPS: fed with a basal diet supplemented with 75 mg/kg ANT, and injected with 0.5 mg/kg LPS; LA+LPS: fed with a basal diet supplemented with 1000 mg/kg LA, and injected with 0.5 mg/kg LPS. N=8 in each group. (A) Weight loss. Weight loss was calculated using the equation: weight on day 42 - weight on day 44. (B) Pictures of the jejunal and ileal lumen. The arrows indicates the hemorrhagic spots. (C) Histomorphometric analysis of the jejunum by Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) staining. 40× magnification, scale bar: 200μm. (D) Ileum histomorphometric analysis. 100× magnification, scale bar: 100μm. The villus height and crypt depth shown in the pictures were randomly measured in 10 visual fields in each sample from each group. The data shown as mean ± SEM were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.