Figure 2.
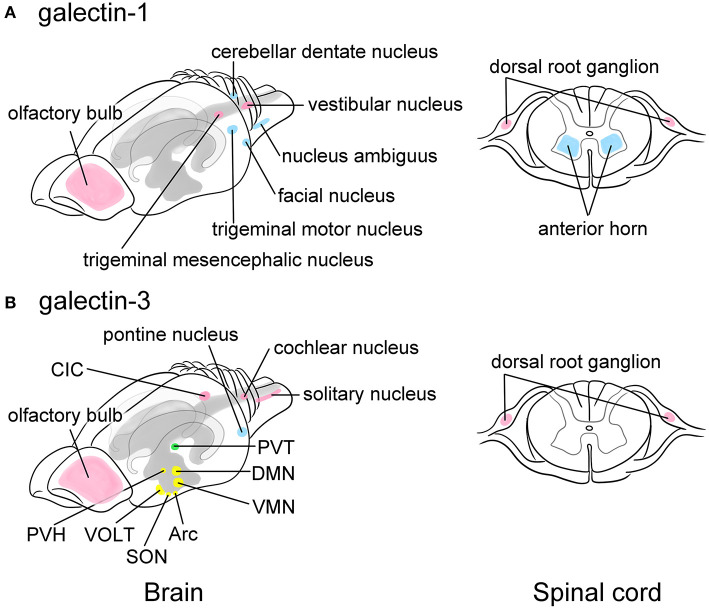
Schematic images showing the predominant localization of galectin-1 (A) and -3 (B) in neurons of the adult rat brain (left) and the spinal cord (right). Galectin-1 is predominantly localized to motoneurons or neurons controlling voluntary movements such as the facial nucleus, the trigeminal motor nucleus, the nucleus ambiguus, and the cerebellar dentate nucleus in the brain stem as well as the anterior horn of the spinal cord (blue in A). Certain sensory neurons, including the trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus and the vestibular nucleus in the brain and the neurons in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) also contain galectin-1 (pink in A). Galectin-3 is abundant in the arcuate nucleus (Arc) and the dorsomedial nucleus (DMN), and moderately expressed in the ventromedial nucleus (VMN), the supraoptic nucleus (SON), and the paraventricular nucleus (PVH) in the hypothalamus that play central role in the regulation of appetite control, endocrine/autonomic system, and stress response (yellow in B). Galectin-3 is also present in the vascular organ of the lamina terminalis (VOLT), one of the sensory circumventricular organs (yellow in B). The paraventricular nucleus in the thalamus (PVT) related to the emotion also highly expresses galectin-3 (green in B). Other nuclei such as the central nucleus of inferior colliculus (CIC), the cochlear nucleus, and the solitary nucleus also express galectin-3 (pink in B), suggesting its role in the regulation of taste and hearing sensing. Similar to galectin-1, the primary sensory neurons in the DRG express galectin-3 (pink in B). The pontine nucleus regulating voluntary movements also contains abundant galectin-3 (blue in B). Olfactory bulb expresses both galectins (pink in A and B). Motoneurons and neurons involved in movement are represented in blue, sensory-related neurons are in pink, and the neurons regulating endocrine/autonomic functions are indicated in yellow, and nucleus related to higher brain function is labeled in green. The cerebral ventricles are indicated in gray and the hippocampus is bordered in light gray. This figure is created based on the in situ hybridization data by Hynes et al. (1990) for galectin-1 and immunohistochemical data by Yoo et al. (2017) for galectin-3. For detailed localization of galectins in the rat brain, please refer their manuscripts. For data of the mouse and human brain, please visit Allen Brain Map (https://portal.brain-map.org).