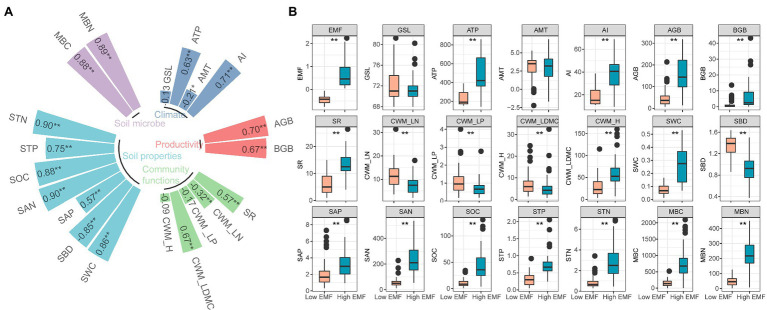
Figure 2.
Characteristics of ecosystem multifunctionality and environmental factors. (A) Relationship among ecosystem multifunctionality and climate, productivity, community functions, soil properties, soil microbial factors, and the value in the square represents the value of the correlation coefficient between each factor with ecosystem multifunctionality. * and ** show the significant correlations at 0.05 and 0.01 levels. (B) Difference of low and high ecosystem multifunctionality combined with environmental factors. Statistical significance between low and high ecosystem multifunctionality conditions was assessed by one-way ANOVA analysis. **p<0.01. EMF, ecosystem multifunctionality; GSL, start of growing season to the peak of growing season; ATP, annual total precipitation (mm); AMT, annual mean temperature (°C); AI, aridity index; AGB, aboveground biomass (gm−2); BGB, belowground biomass (gm−2); SR, species richness; CWM_LN, community-weighted mean value of leaf nitrogen; CWM_LP, community-weighted mean value of leaf phosphorus; CWM_LDMC, community-weighted mean value of leaf dry matter content; CWM_H, community-weighted mean value of plant height; SWC, soil water content (%); SBD, soil bulk density (gcm−3); SAP, soil available phosphorus content (mgkg−1); SAN, soil available nitrogen content (mgkg−1); SOC, soil organic carbon content (gkg−1); STP, soil total phosphorus content (%); MBC, microbial biomass carbon content (mgkg−1); MBN, microbial biomass nitrogen content (mgkg−1).