Figure 1.
iPSC differentiations
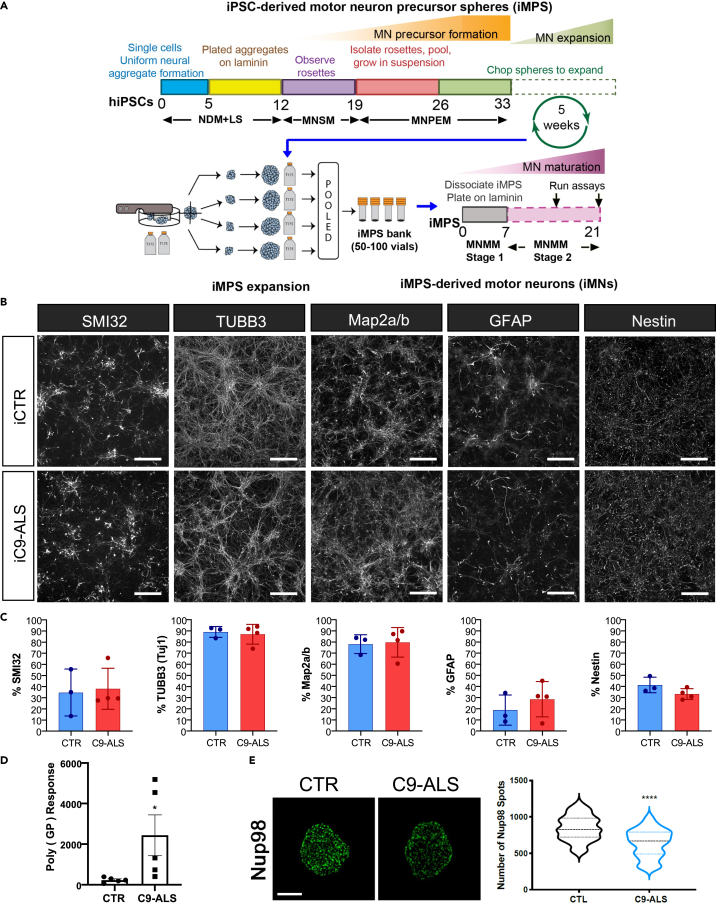
(A) Schematic of protocol for iPSC differentiation into motor neuron cultures used by NeuroLINCS for transcriptomics, proteomics, and epigenomics assays. The iPSC-derived motor neuron precursor spheres (iMPS) were dissociated into single cells from C9-ALS and healthy patient iPSC lines and plated on laminin substrate to differentiate further into motor neuron (iMN) cultures over 21 days.
(B) Representative images of iMNs from control (25iCTR) and C9-ALS (52iALS). iMNs show consistent distribution of neural cell populations marked by SMI32, TuJ1, Map2a/b, GFAP, and nestin. Scale bars are 50 μm.
(C) Levels of SMI32, TUBB3 (TuJ1), GFAP, nestin, and Map2a/b in control and C9-ALS iMN cultures from the individual iPSC lines. Two-sided unpaired t test with Welch's correction (CTR n = 3 and C9-ALS n = 4).
(D) Poly(GP) DPR levels as determined by MSD ELISA assay in iMNs (from CS29 ISO 191.06, CS52 4544.25, CS0702 60.45, CS7VCZ 5180.33, CS29 405.69, CS0465 297.85, CS0594 391.5, CS0BUU 1323.32, CS52 ISO 233.72, CS6ZLD 738.54). p = 0.0348.
(E) Maximum intensity projections from SIM imaging of Nup98 in nuclei isolated from control and C9ORF72 iMNs (CS0188, CS0594, CS0702, CS29, CS52, CS7VCZ). Quantification of Nup98 spots. N = 3 control and 3 C9ORF72 iPSC lines, 20 NeuN+ nuclei/line. Student’s t test was used to calculate statistical significance (Gendron et al., 2017). p < 0.0001. Scale bar, 5 μm.