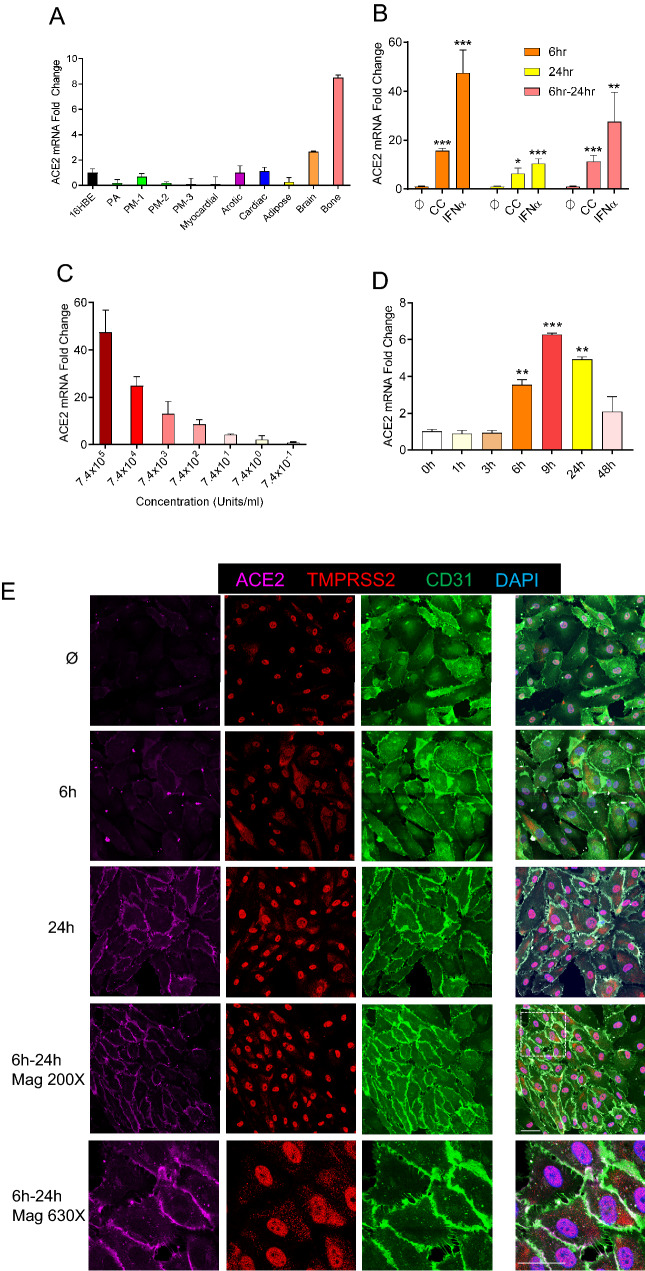
Fig. 4.
IFNα induces ACE2 in human primary endothelial cell cultures. A Relative mRNA expression of ACE2 in different types of human endothelial cells, including the pulmonary arterial (PA), three pulmonary microvasculature (PM -1, -2, -3), myocardium (Myocardial), aorta (Aortic), cardiac microvascular (Cardiac), white adipose(Adipose), brain microvasculature (Brain) and bone (Bone). Endothelial expression is relative to that from the 16HBE human bronchial epithelial cell line (16HBE). Means ± SEM are from two technical replicates. B Relative mRNA expression of ACE2 in human pulmonary arterial endothelial cells (PAECs) when incubated in cytokine-free media (ϕ); with a cytokine cocktail (CC—consisting of IFNα, IFNγ, TNFα, IL6 & CXCL10); or with IFNα alone for 6, 24 and 6–24 h (a total of 6 h simulation and then total RNA collect in 24 h). ACE2 expression level in cytokine-free media were used as control. Means ± SEM derived from three biological replicates. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to untreated control, unpaired t test. C IFNα dose-dependent mRNA expression of ACE2 in human PAEC. Fold-change of ACE2 expression is relative to that in untreated cells. Means ± SEM are from two biological replicates. D Relative mRNA expression of ACE2 in human PMVEC after IFNα incubation for 1, 3, 6, 9, 24 and 48 h, in a time-dependent manner. Means ± SEM are from two biological replicates. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to untreated control (0 h), unpaired t test. E Immunofluorescence for ACE2 (magenta) TMPRSS2 (red) and CD31 (green) in PAECs treated or not with IFNα (7.4 × 105 units/mL) for 6, 24 and 6–24 h. Zoomed insets showing ACE2 expression on the cell membrane (630X magnification). Bar = 20 µm