Figure 7.
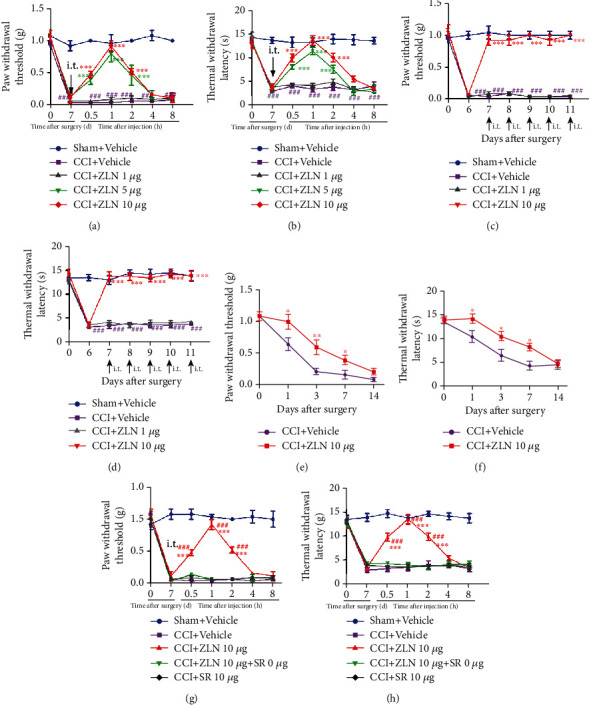
Effect of ZLN005 on the treatment and prevention of mechanical pain and hyperalgesia after CCI. (a, b) A single injection of ZLN005 (1 μg, 5 μg, and 10 μg/5 μL, i.t.) or vehicle (5 μL) was given on day 7 following CCI (∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared with the CCI+vehicle group). In contrast, the CCI+vehicle group had no significant change in PWT and TWL (###P < 0.001 compared with the sham+vehicle group). No significant difference in the baseline thresholds was observed among all groups (n = 5 per group). (c, d) ZLN005 (1 μg and 10 μg/5 μL, i.t.) or vehicle (5 μL) was given for 5 consecutive days from day 7 to day 11. Treatment with ZLN005 (10 μg) significantly reversed PWT and TWL in CCI mice (∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared with the CCI+vehicle group). In contrast, the CCI+vehicle group had no significant change in PWT and TWL (###P < 0.001 compared with the sham+vehicle group) (n = 5 per group). (e, f) Preventive effect of ZLN005 on the development of CCI. ZLN005 (10 μg, i.t.) was given once daily from day 0 to day 2 after CCI. The pain behavioral tests were performed before CCI and on day 1, day 3, day 7, and day 14 after CCI. Treatment with ZLN005 (10 μg, i.t.) significantly elevated the PWT and TWL at day 3 and day 7 after CCI. However, no significant difference was observed on day 14 (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared with CCI+vehicle mice) (n = 5 per group). (g, h) The analgesic effect of ZLN005 in CCI mice was completely inhibited by the PGC-1α inhibitor SR-18292 (SR). Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures was performed, followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test (∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared with the sham+vehicle group, ###P < 0.001 compared with the CCI+ZLN+SR group, n = 5 per group).
