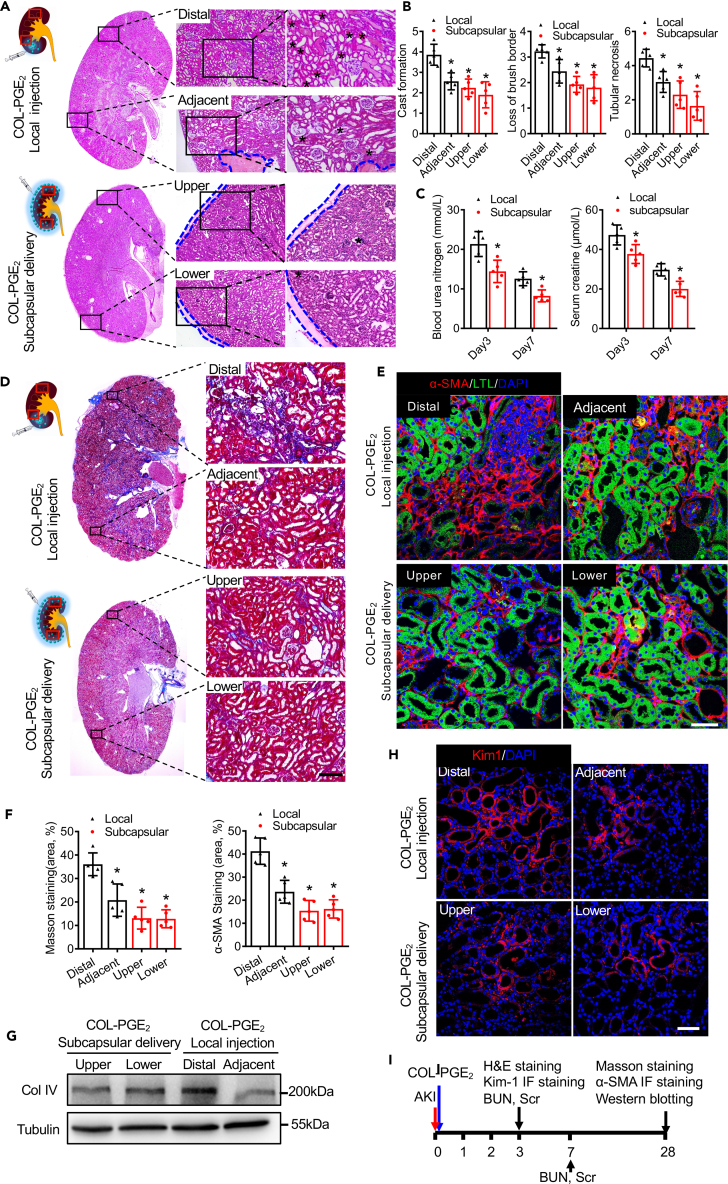
Figure 2.
Subcapsular delivery of the COL-PGE2 matrix is superior to local injection in kidney recovery
(A) Histological analysis of kidney injury by H&E staining on day 3 post-AKI. Top: COL-PGE2 matrix local injection; bottom: COL-PGE2 matrix subcapsular delivery. Massive necrosis is observed in proximal tubules with hyaline casts (asterisks), and subcapsular delivery of the COL-PGE2 matrix is superior to local injection for kidney recovery. The blue dotted lines indicate the edges of the COL-PGE2 matrix. Rectangles in schema represent Distal, Adjacent (upper panel) and Upper, Lower (lower panel), respectively. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(B) Quantification of typical pathological changes, such as cast formation, tubular necrosis, and loss of the brush border.
(C) Serum blood levels of urea nitrogen (left) and creatinine (right) were measured at different time points after AKI.
(D) Representative images of kidney sections stained with Masson trichrome stain on day 28 after AKI. Rectangles in the schema represent Distal, Adjacent (upper panel) and Upper, Lower (lower panel), respectively. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(E) Representative images of α-SMA (red) immunofluorescence staining on day 28 after AKI. The proximal tubules were co-stained with Lotus Tetragonolobus Lectin (LTL; green). Scale bars, 50 μm.
(F) Quantitative analysis of Masson trichrome staining (left) and the α-SMA+ staining area (right) were performed to evaluate renal fibrosis.
(G) Immunoblot analysis of type IV collagen (Col IV) protein in the kidney on day 28 after AKI.
(H) Representative images of Kim-1 (red) immunofluorescence staining on day 3 after AKI. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(I) Schematics of the time lines for each experiment. One-way repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests (B, C, and G) was used for statistical analysis. Data are expressed as mean ± SD; n = 5, ∗p < 0.05 versus distal positions of the local injection of the COL-PGE2 matrix local injection.