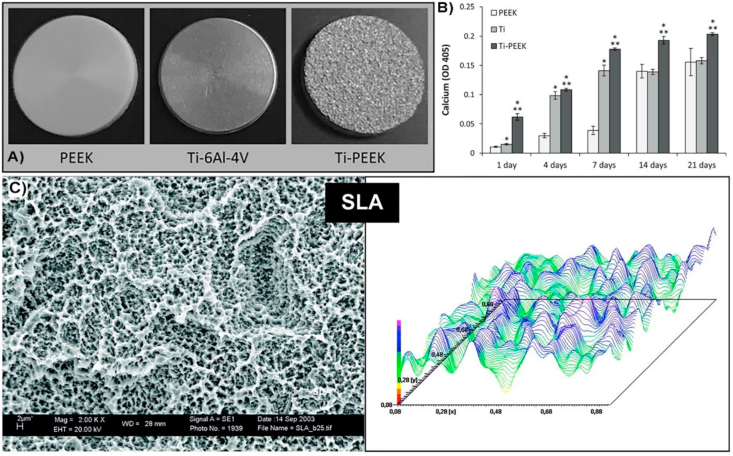
Fig. 7.
Ti-PEEK spinal implants with hierarchical roughness. A) Pictures of implanted samples used to study the influence of hierarchical roughness with calcium deposition compared to other surfaces and B) Graph showing in vitro variations in the calcium deposition comparing the 3 implanted surfaces, showing the Ti-PEEK implant (TyPEEK, Tyber Medical) with the highest increased calcium deposition in presence of human osteoprogenitor cells [117]. Copyright 2019, Science Direct, under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International. C) Right: SEM image of micro and nanoscale topography achieved using SLA on coated titanium plasma-sprayed PEEK for spinal implants. The hierarchical structure is composed by cavities with diameters of wider indentations of about 10–50 μm completely superposed by smaller pores of about 1–2 μm diameter. Left: profilometric contact style topography representing the surface waviness. Figure modified from [116]. Copyright 2005, John Wiley and Sons Inc.