FIGURE 2.
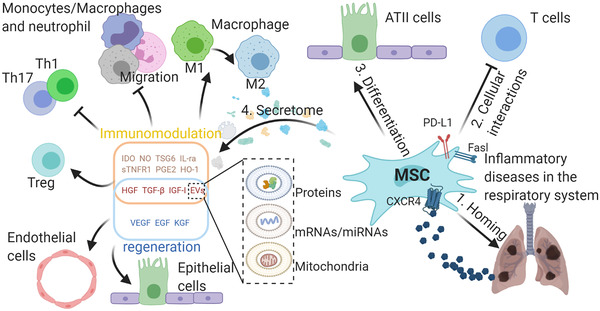
Properties of MSCs in typical inflammatory diseases in respiratory system. Exogenous imported MSCs can migrate to damaged tissues through the SDF‐1‐CXCR4 axis. MSCs can differentiate into ATII‐like cells and inhibit immune cells by cellular interactions and secret a variety of bioactive molecules which have immunomodulation abilities and can promote regeneration of the damaged tissue. The molecules associated with immunomodulation can shift macrophages from M1 to M2 phenotype, inhibit the migration of macrophages, neutrophil, and monocytes, inhibit the differentiation of TH1 and TH17 cells, and promote the formation of Treg cells. The growth factors can protect alveolar epithelial cells and pulmonary vascular endothelial cells from damage. MSCs can transport proteins, mRNAs/miRNAs, and mitochondria to other cells through EVs to exert its functions in immunomodulation and regeneration. The function of EVs is determined by its contents
