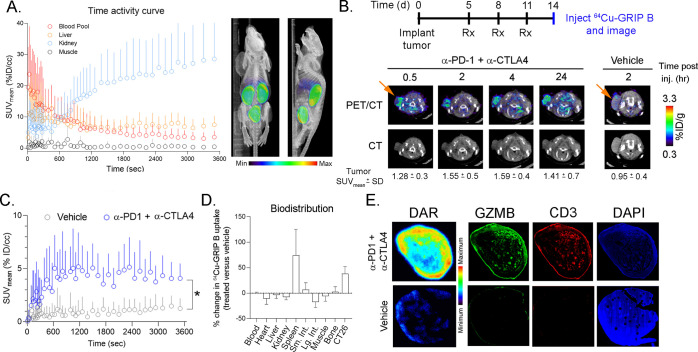
Figure 3.
64Cu-GRIP B detects T cell activation in vivo elicited by an immune checkpoint inhibition. (A) A time activity curve showing the renal clearance of 64Cu-GRIP B in a male balb/c mouse bearing a subcutaneous CT26 tumor. (B) Representative transaxial CT and PET/CT images showing the accumulation over time of 64Cu-GRIP B in a CT26 tumor exposed to anti-PD1 and anti-CTLA4 CPI. Also shown is the uptake of 64Cu-GRIP B in a tumor-bearing mouse treated with a vehicle. (C) A time activity curve from a dynamic PET acquisition showing the tumoral uptake of 64Cu-GRIP B in CT26 tumors from mice treated with a vehicle or CPI. *P < 0.05. (D) A plot showing the percentage change in 64Cu-GRIP B uptake per organ in treated vs untreated mice. (E) Digital autoradiography and immunofluorescence showing the colocalization of 64Cu-GRIP B with GZMB and T cells within CT26 tumor slices from mice exposed to a vehicle or CPI.