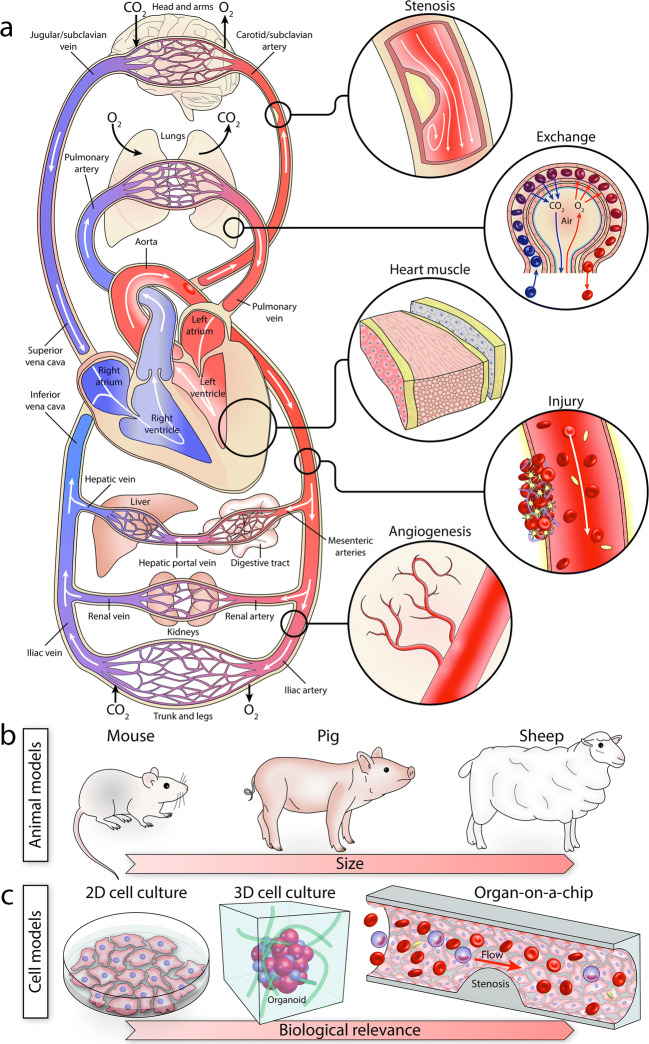
Fig. 1.
a Schematic of the human circulatory system, consisting of the heart at the center and a complex network of vessels which interact with other organs. b Animal models are extensively used for studying the human circulatory system. c The complexity, cost, and inherent differences between the human and animal models have led to the evolution of cell models, ranging from simple 2D models (Petri dish, flasks) to more complex 3D models (hydrogel, spheroids, organoids) and more physiologically relevant microfluidic models