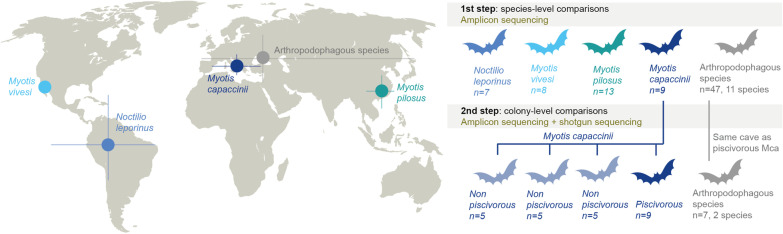
Fig. 1.
Map of the approximate distributional range (latitude and longitude limits) of bats analysed in this study (left), and species and number of individuals (n) used in each step of the analysis (right). In the first step, 37 bats from four well-known fish-consuming colonies of the four piscivorous species were compared to 47 bats belonging to 11 strict arthropodophagous species. In the second step, we increased the resolution of the analyses in the piscivorous bat Myotis capaccinii, by adding more individuals (n = 15) from three allegedly non-piscivorous colonies to the analysis. For these analyses we also included arthropodophagous bats that roost in the same cave as the piscivorous M. capaccinii, namely Miniopterus schreibersii and Myotis myotis as controls