Fig. 3.
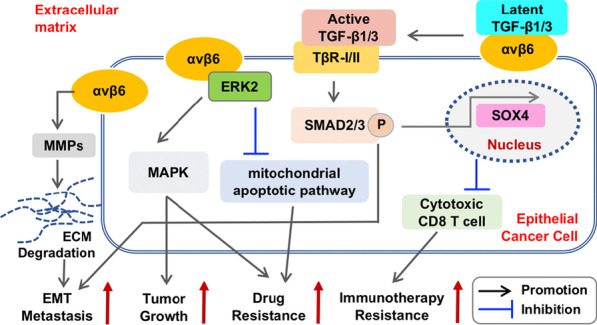
Integrin αvβ6 signalosome in tumor progression. Studies have suggested multiple pro-tumorigenic roles of αvβ6 integrin, involving distinct downstream pathways, in accelerating tumor progression. For example, the αvβ6 integrin can facilitate cancer cell invasiveness and thus metastasis via increasing MMPs secretion and ECM degradation. By interacting with ERK2, αvβ6 activates MAPK signaling to increase cell proliferation and tumor growth, and to inhibit 5-FU-induced cancer cell apoptosis through suppression of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway (by impairing the cytochrome C release, decreasing the activity of caspase-3 and caspase-9, and upregulating the anti-apoptotic factor BCL-2), leading to drug resistance. Furthermore, the αvβ6 integrin can interact with latent TGFβ and subsequently activate TGFβ-linked pathways to positively contribute to EMT process and metastasis. Alternatively, the activated TGFβ signaling drives expression of cancer stemness factors (e.g., SOX4) to evade immunotherapy. Lines with arrows and perpendicular denote a promotion or an inhibition effect, respectively. P within the circle denotes phosphorylation. See text for details
