Figure 1.
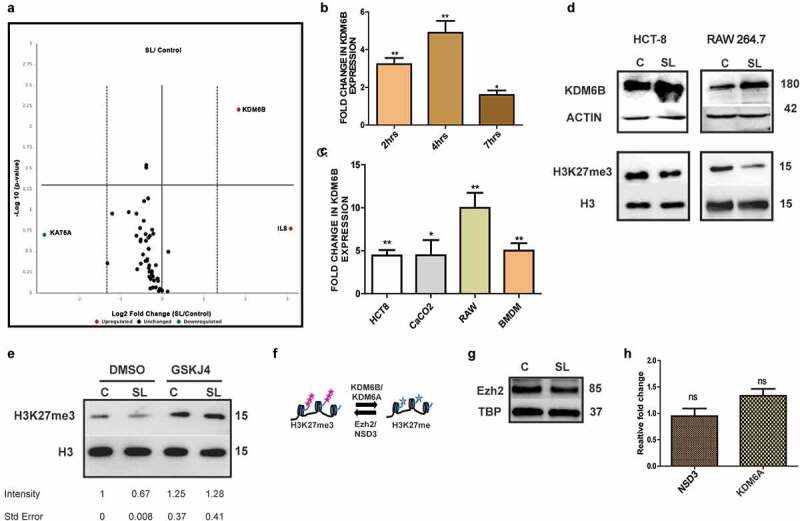
KDM6B recruitment and concomitant loss of H3K27me3 mark upon Salmonella Typhimurium infection [A.] Volacano plot showcasing fold change in expression profile of selected epigentic modifier in adenocarcinoma cell line HCT-8 post 4h of Salmonella Typhimurium (SL (SL1344 strain)) infection versus control cells.[B] Expression analysis of KDM6B at different time points post SL infection in HCT-8 cells and [C] in different cell lines post 4h of SL infection (p.i.) represented in fold change values by Quantitative Real Time PCR (qPCR) HPRT (Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase) was used for normalization [D.] Immunoblots showcasing KDM6B and respective Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3 status at 4h p.i. in HCT-8 and RAW 264.7 cells.[E.] Immunoblot representing H3K27me3 upon SL infection upon treatment with KDM6B demethylase inhibitor GSKJ4 (30 µM) in RAW264.7 cells as indicated with respective fold intensity mentioned below. [F.] Pictorial representation of epigenetic modifiers (enzymes) involved in maintenance of H3K27me3 mark in cells. Immunoblot represeting expression levels of H3K27me3 methyltransferase Ezh2 [G] and NSD3 [H] using qRT-PCR at 4h post SL infection. KDM6A expression levels at 4h post SL infection analyzed using qRT-PCR (HPRT was used for normalization) [H]. TBP, Actin, H3 were used as loading control as indicated. Statistical significance was analyzed using unpaired t-test (’**’ p-value <.01, ‘*’ p- value <.05)
