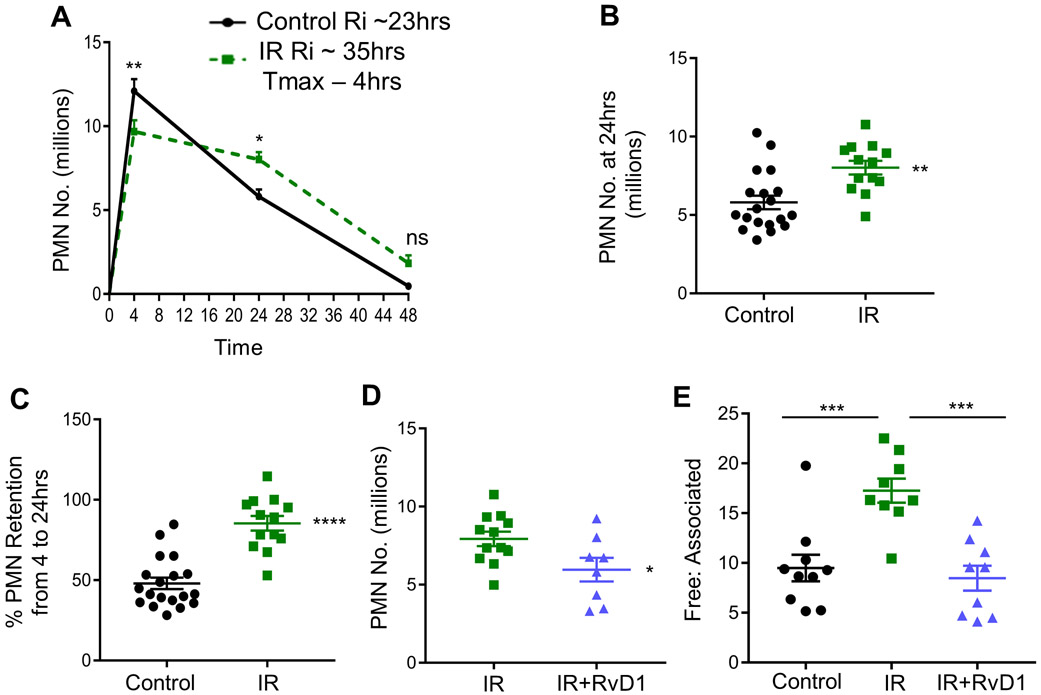
Fig. 1. Inflammation-resolution is defective in sublethally irradiated mice.
(A) C57BL/6 mice were subjected to mock or sublethal radiation as described in the methods section. Peritoneal exudates were collected 4, 24 and 48 hrs post ZymA injection (200 μg/mouse). Cells were enumerated and PMN were analyzed by flow cytometry. Results are n = 4 separate cohorts, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns - non-significant, Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test. (B) PMN number at 24 hrs post ZymA injection were analyzed, **p<0.01, Student’s t-test. (C) The percentage of retained PMN in the peritoneum were calculated, ****p<0.0001, Student’s t-test. (D) Vehicle or 300 ng of RvD1 was i.p. injected simultaneously with ZymA and PMN number was enumerated 24 hrs post injection, *p<0.05, Student’s t-test. (E) Efferocytosis was assessed by calculating the ratio of free to associated PMN at 24 hrs post ZymA injection, ***p<0.001, One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. All results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M, and each symbol represents an individual mouse.