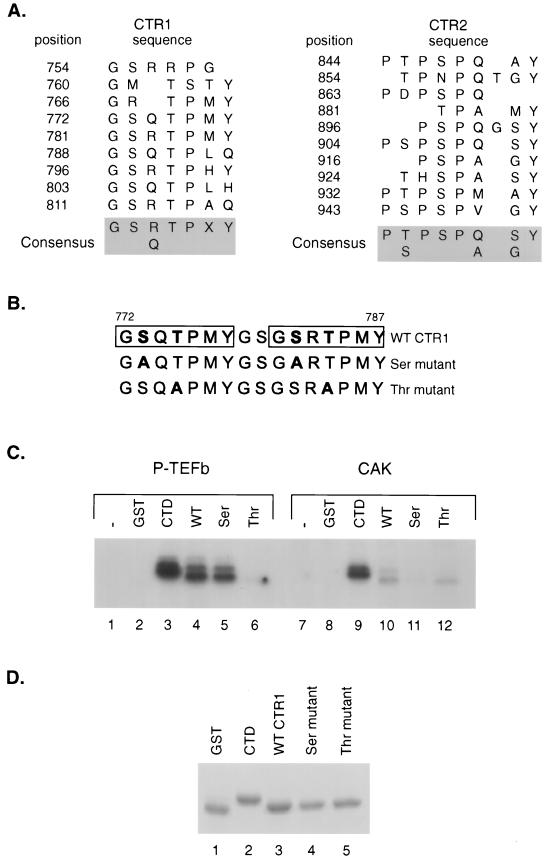
FIG. 7.
Comparison of P-TEFb and CAK phosphorylation of SPT5 CTR1 repeats. (A) Sequences of CTR1 and CTR2 repeats. The positions of the C-terminal repeat motifs in the CTR1 and CTR2 domains of SPT5 are indicated, as is the consensus sequence for each domain, as previously described (49). (B) The sequences of the two CTR1 repeats that were fused to GST and used as substrates in in vitro kinase reactions are shown. The boxes indicate the positions of the repeats, and the mutated amino acids are shown in boldface type. (C) In vitro kinase reactions were performed using baculovirus-produced and purified CDK9-cyclin T1 (lanes 1 to 6) or the baculovirus-produced and purified CAK components including CDK7, cyclin H, and MAT1 (lanes 7 to 12). The kinase reactions were performed without the addition of substrate (lanes 1 and 7) or following the addition of GST (lanes 2 and 8), a GST-CTD fusion protein containing two repeats of the RNA polymerase II CTD (lanes 3 and 9), or GST fusion proteins containing two CTR1 repeats with either the wild-type (WT) sequences (lanes 4 and 10), serine residues substituted for alanine (lanes 5 and 11), or threonine residues substituted for alanine (lanes 6 and 12). (D) A Coomassie blue-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel of the GST fusion proteins that were used as substrates for kinase assays in panel B is shown.