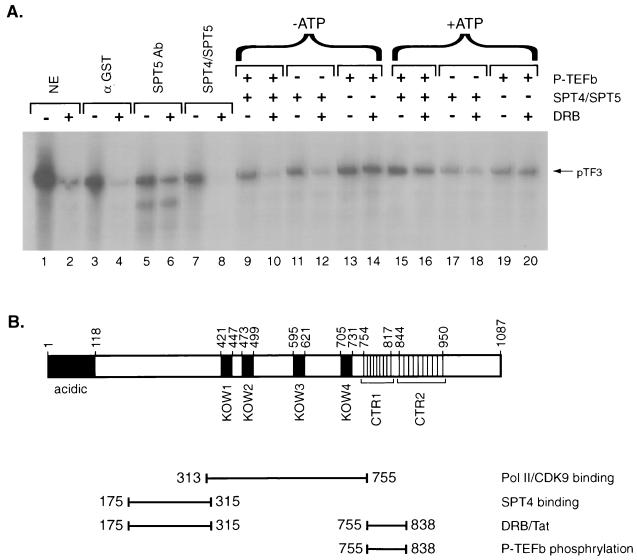
FIG. 8.
Role of P-TEFb phosphorylation on SPT4-SPT5 function in mediating DRB repression. (A) In vitro transcription assays were performed with the pTF3-6C2AT template in the presence (even-numbered lanes) or absence (odd-numbered lanes) of DRB. Untreated HeLa nuclear extract (lanes 1 and 2), HeLa nuclear extract immunodepleted with GST antibody (lanes 3 and 4), or HeLa nuclear extract immunodepleted with SPT5 antibody (lanes 6 to 20) were used in the in vitro transcription assays. In vitro transcription assay mixtures with the SPT5-immunodepleted HeLa nuclear extracts were supplemented with the SPT4-SPT5 complex purified following baculovirus expression in the absence of other treatment (lanes 7 and 8), the SPT4-SPT5 complex preincubated with P-TEFb (lanes 9 and 10 and lanes 15 and 16), the SPT4-SPT5 complex preincubated without P-TEFb (lanes 11 and 12 and lanes 17 and 18), or P-TEFb alone preincubated in the absence of SPT4-SPT5 (lanes 13 and 14 and lanes 19 and 20). The preincubation procedure was performed in the absence of ATP (lanes 9 to 14) or in the presence of 5 mM ATP (lanes 15 to 20), which was subsequently removed by dialysis. (B) A schematic of the functional domains in the SPT5 protein that were analyzed in this study is shown.