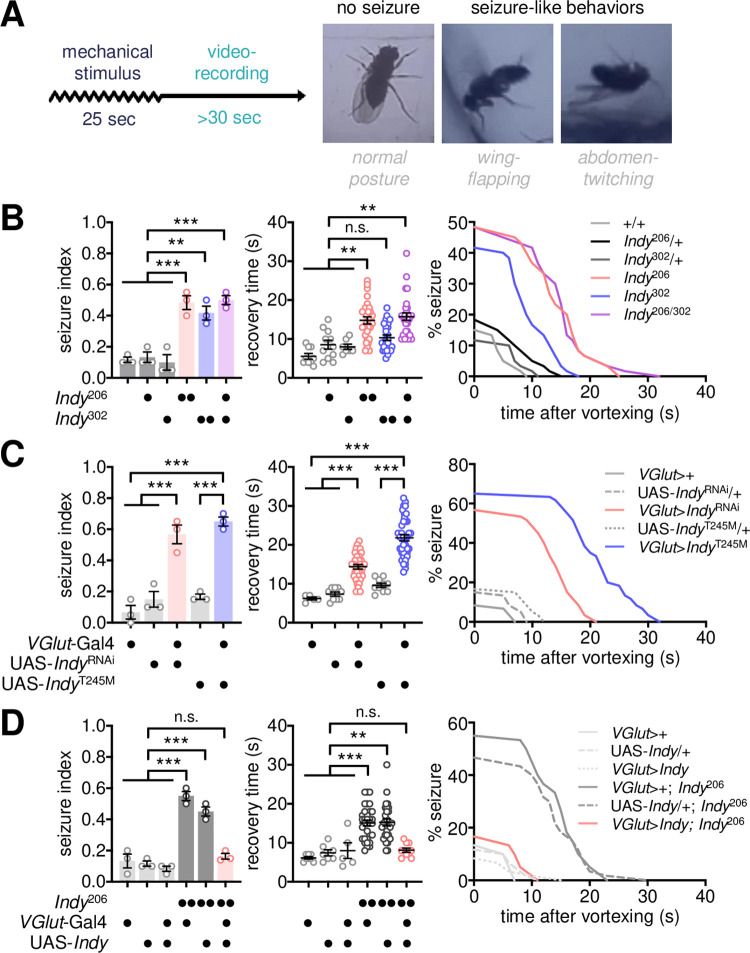
Fig 1. Loss of Indy function in glutamatergic neurons induces BSS.
(A) Experimental design for the quantitative analysis of bang-induced seizure-like behaviors in Drosophila. A group of flies (n = 5) was vortexed for 25 s, after which post-stimulus responses were video recorded. Seizure-like behaviors, including wing-flapping and abdomen-twitching, were scored in individual flies. (B) Quantitative analyses of BSS in Indy mutants homozygous or trans-heterozygous for loss-of-function alleles. A seizure index was calculated as the ratio of the number of BSS-positive flies to the total number of flies tested in each experiment (n = 20; 5 flies per group × 4 groups per experiment) and averaged from three independent experiments. Recovery time was calculated individually for BSS-positive flies as the latency to normal posture after vortexing and was averaged for each genotype (n = 7–29 flies). Percent seizure was calculated as the percentage of BSS-positive flies per genotype at each second after vortexing (n = 60 flies; 20 flies per experiment × 3 experiments). Data represent means ± SEM. n.s., not significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, as determined by one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (seizure index) or by Kruskal Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (recovery time). (C) Silencing of Indy function in glutamatergic neurons by transgenic overexpression of IndyRNAi or KTS-associated IndyT245M is sufficient to induce BSS. Quantitative analyses of BSS in individual flies were performed as described above. Data represent means ± SEM (seizure index, n = 60 flies in 3 independent experiments; recovery time, n = 5–39 flies). ***P < 0.001, as determined by one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Transgenic overexpression of wild-type INDY in glutamatergic neurons rescues BSS in Indy mutants. Data represent means ± SEM (seizure index, n = 60 flies in 3 independent experiments; recovery time, n = 5–33 flies). n.s., not significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, as determined by two-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test.