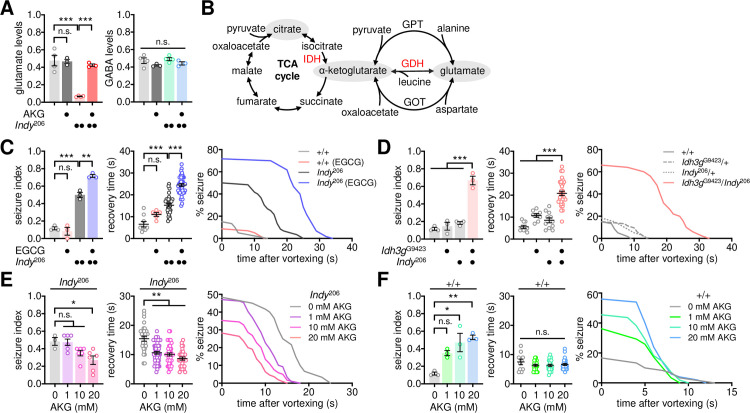
Fig 3. Indy-dependent BSS involves a metabolic link between the TCA cycle and glutamate transmission.
(A) Indy mutants display low levels of free glutamate that are rescued by oral administration of α-ketoglutarate (AKG). Flies were fed control or AKG-containing food (20 mM) for 3 d before harvesting. Free amino acids in whole-body extracts were quantified using ion-exchange chromatography. Relative levels of glutamate and GABA were calculated by normalizing to glycine levels. A significant Indy x AKG interaction effect on glutamate levels (P = 0.0006) was detected by two-way ANOVA. Data represent means ± SEM (n = 3–4). n.s., not significant; ***P < 0.001, as determined by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. (B) Glutamate biosynthesis via the TCA cycle. IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; GPT, glutamate-pyruvate transaminase; GOT, glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase. (C) Oral administration of the GDH inhibitor epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) exaggerates BSS phenotypes in Indy mutants. Flies were fed control or EGCG-containing food (5 mg/ml) for 3 d before the BSS assessment. Quantitative analyses of BSS in individual flies were performed as described in Fig 1. Two-way ANOVA detected a significant Indy x EGCG interaction effect on seizure index (P = 0.0025). Data represent means ± SEM (seizure index, n = 58–60 flies in 3 independent experiments; recovery time, n = 5–43 flies). n.s., not significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, as determined by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Idh3g heterozygosity induces BSS phenotypes in heterozygous Indy mutants. Significant Indy x Idh3g interaction effects on seizure index (P = 0.0002 by two-way ANOVA) and recovery time (P = 0.0086 by Aligned ranks transformation ANOVA) were detected. Data represent means ± SEM (seizure index, n = 50–60 flies in 3 independent experiments; recovery time, n = 8–33 flies). ***P < 0.001, as determined by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (seizure index) or by Wilcoxon rank sum test (recovery time). (E and F) Oral administration of AKG rescues BSS phenotypes in Indy mutants. Flies were fed control or AKG-containing food (20 mM) for 3 d before the BSS assessment. Data represent means ± SEM (seizure index, n = 50–119 flies in 3 independent experiments; recovery time, n = 10–56 flies). n.s., not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, as determined by one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (seizure index), by Welch’s ANOVA with Dunnett’s T3 multiple comparisons test (E, recovery time), or by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons (F, recovery time).