Figure 3. Chemogenetic activation of VTA DA neurons, or VTA-NAc pathway, reverses CFA induced decrease in motivation.
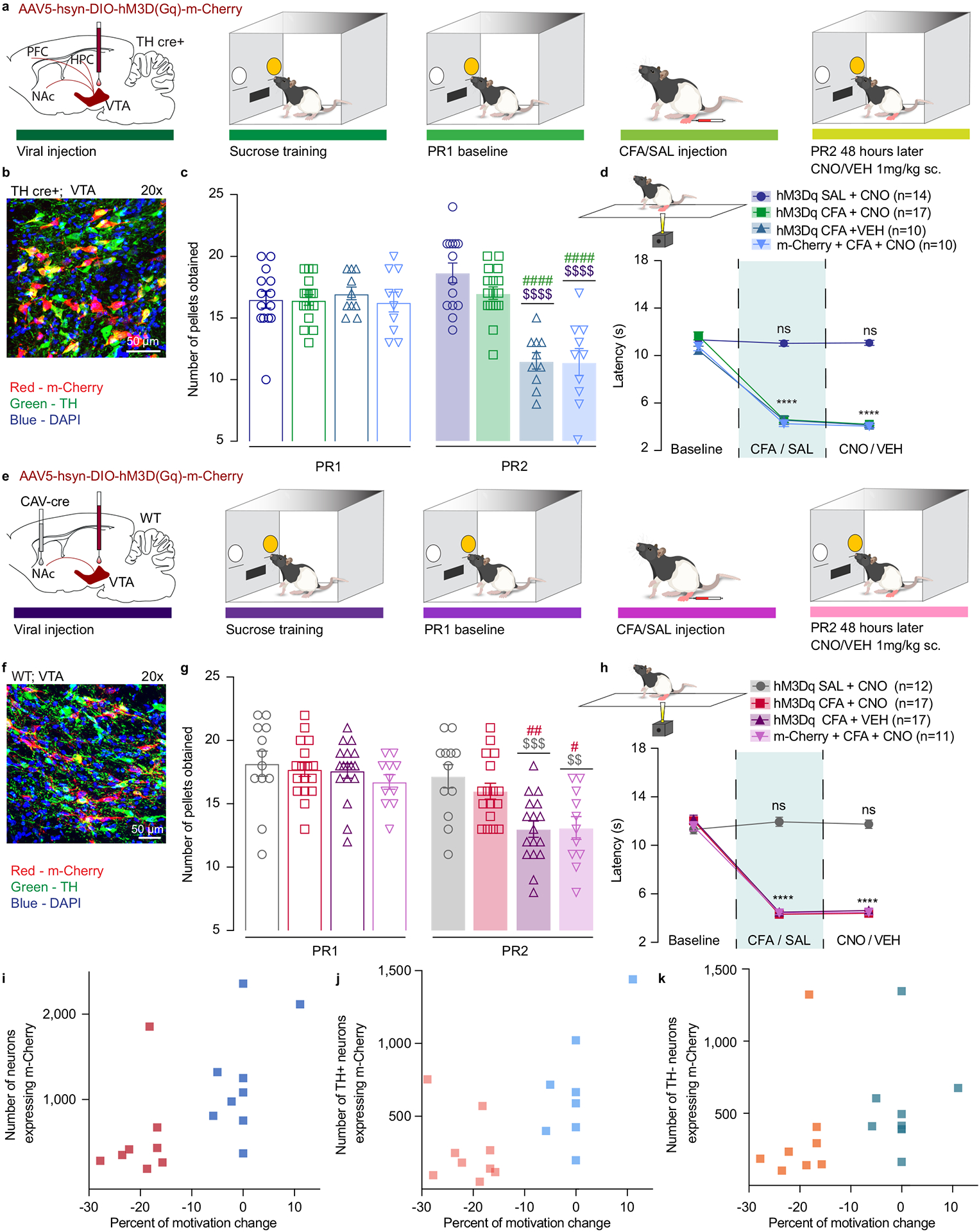
a. Schematic representation of viral injection and behavioral methodology. b. Representative coronal section of VTA Gq DREADD expressing neurons. Blue – DAPI; Red – m-Cherry (Gq DREADD); Green – TH (DA neurons). c. Activation of DA containing neurons in the VTA reverses CFA induced decrease in motivation for sucrose pellets. Animals injected with control virus and CNO alone showed decrease in motivation after the CFA injection (two-way ANOVA for repeated measures, time: F1, 47 = 46.35, p<0.0001; interaction (time × treatment): F3, 47 = 45.18, p<0.0001; Sidak’s post hoc between groups during PR2: hM3Dq + CFA + VEH (n=10) versus hM3Dq + SAL+ CNO (n=14), $$$$ p<0.0001, hM3Dq + CFA + VEH versus hM3Dq + CFA+ CNO (n=17), #### p<0.0001; m-Cherry + CFA + CNO (n=10) versus hM3Dq + SAL+ CNO, $$$$ p<0.0001, m-Cherry + CFA + CNO versus hM3Dq + CFA+ CNO, #### p<0.0001). d. CFA induced hyperalgesia is not altered by activation of DA containing neurons in the VTA (two-way ANOVA for repeated measures, time: F2, 94 = 507.2, p<0.0001; interaction (time × treatment): F6, 94 = 59.72, p<0.0001; Sidak’s post hoc for each group as compared to the group’s baseline session: **** p<0.0001). e. Schematic representation of viral injection and behavioral methodology. f. Representative coronal section of VTA Gq DREADD expressing neurons. Blue – DAPI; Red – m-Cherry (Gq DREADD); Green – TH (DA neurons). g. Activation of NAcSh projecting VTA neurons restores motivation in CFA treated aniamls. Control CFA animals injected with either CNO or virus alone show decrease in motivation (two-way ANOVA for repeated measures, time: F1, 53 = 148.4, p<0.0001; interaction (time × treatment): F3, 53 = 14.66, p<0.0001; Sidak’s post hoc during PR2 between the groups: hM3Dq + CFA + VEH (n=17) versus hM3Dq + SAL+ CNO (n=12), $$$ p=0.0004, hM3Dq + CFA + VEH versus hM3Dq + CFA + CNO (n=17), ## p=0.0085; m-Cherry + CFA + CNO (n=11) versus hM3Dq + SAL+ CNO, $$ p=0.0024, m-Cherry + CFA + CNO versus hM3Dq + CFA + CNO, # p=0.0344). h. CFA-induced hyperalgesia is not altered by activation of VTA-NAc pathway. (two-way ANOVA for repeated measures, time: F2, 106 = 597.4, p<0.0001; interaction (time × treatment): F6, 106 = 74.90, p<0.0001; Sidak’s post hoc for each group as compared to the group’s baseline session: **** p<0.0001). i–k. Bimodal distribution of the animal’s performance during second PR session is observed in hM3Dq + CFA + CNO test group (p=0.0312, Hartigan dip test, number of shuffles 20 000). The percent of motivation change is corelated with the infection rate of the virus. (total number of VTA-NAc m-Cherry expressing neurons r=0.6292, p=0.0068, n=17 rats, Spearman correlation test; the number VTA-NAc m-Cherry expressing neurons positive for TH r=0.7446, p=0.0006, n=17 rats, Spearman correlation test; number of m-Cherry expressing TH negative neurons r=0.539, p=0.0256, n=17 rats, Spearman correlation test). The data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m.
