Figure 6. RMTg GABAergic neuronal projections have higher release probability in CFA treated animals.
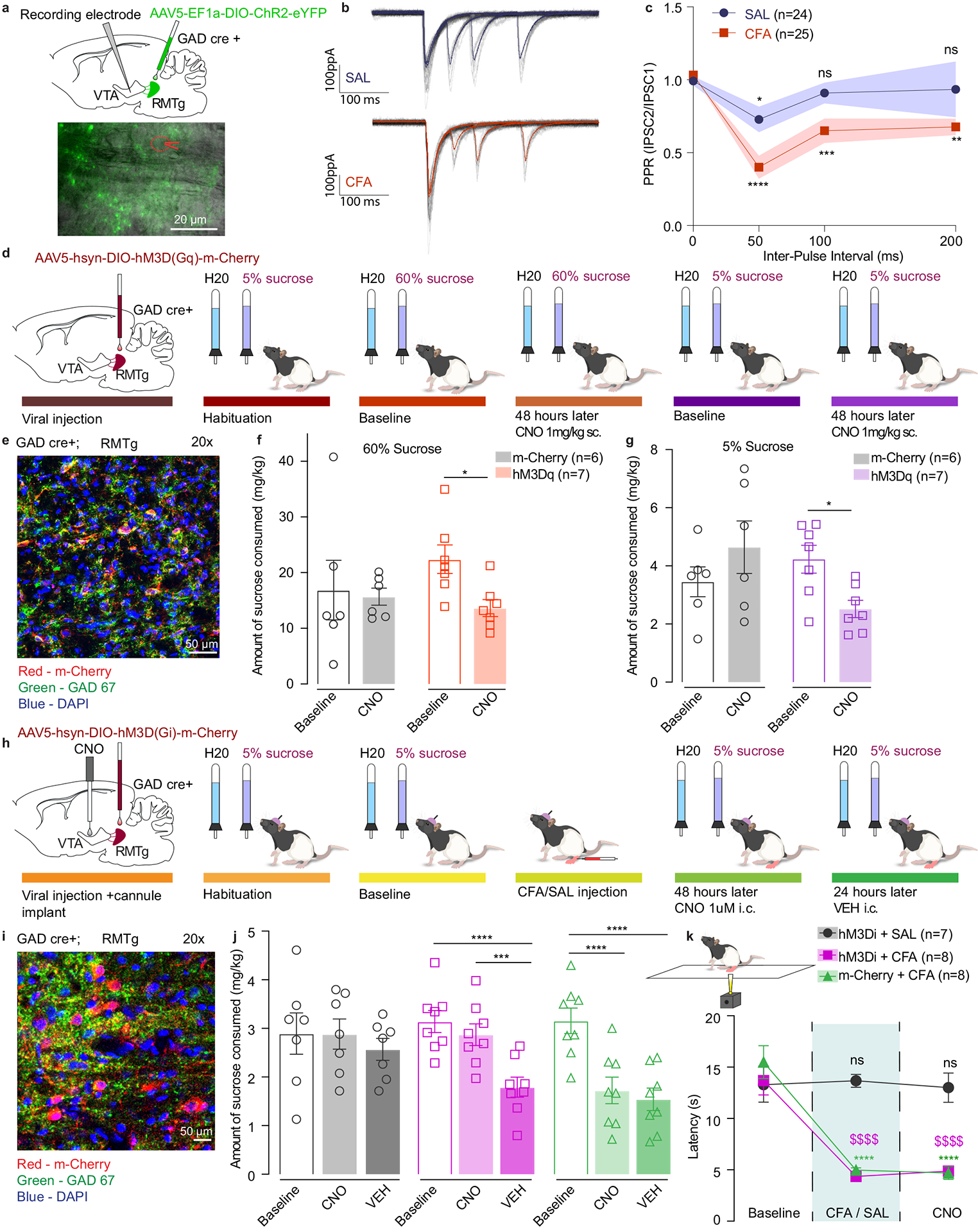
a. Representative image of viral injection in the RMTg and recording electrode in the VTA of GAD-cre animals. b. Representative traces of evoked IPSCs in control (saline) and pain (CFA) condition represented as mean ± s.e.m.. c. PPR is persistently depressed in the condition of pain which is consistent with a higher release probability. (2way ANOVA for repeated measures; inter-pulse interval: F3, 141 = 12.32, p<0.0001; interaction (inter-pulse interval × treatment): F3,141 = 2.479, p=0.0637; Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post hoc test comparing PPR at each inter-pulse interval to the baseline: SAL, *p=0.0363; CFA, **p = 0.0022; ***p=0.0009; **** p<0.0001, n (SAL) = 24 cells from 4 rats, n (CFA) = 25 cells from 3 rats, data represented as mean ± s.e.m.) d. Schematic representation of behavioral methodology. e. Representative coronal section of RMTg Gq DREADD expressing neurons. Blue – DAPI; Red – m-Cherry (Gq DREADD); Green – GAD 67 (GABA neurons). f. Activation of GABA containing neurons in the RMTg induces decrease in the amount of 60% sucrose consumed (open bars-baseline, filled bars – 48 hours post CNO. 60% two-way ANOVA for repeated measures, time: F1, 11=4.816, p=0.0506; interaction (time × treatment): F1, 11=2.786, p=0.1233; Sidak’s post hoc within group: hM3Dq (n=7) baseline versus 48 hours post CNO, * p=0.0317). g. Activation of GABA containing neurons in the RMTg induces decrease in the amount of 5% sucrose consumed (open bars-baseline, filled bars – 48 hours post CNO. 5% two-way ANOVA for repeated measures, time: F1, 11=0.3548, p=0.5635; interaction (time × treatment): F1, 11=10.96, p=0.0069; Sidak’s post hoc within group: hM3Dq (n=7) baseline versus 48 hours post CNO, * p=0.03). h. Schematic representation of behavioral methodology. i. Representative coronal section of RMTg Gi DREADD expressing neurons. Blue – DAPI; Red – m-Cherry (Gi DREADD); Green – GAD 67 (GABA neurons). j. Inhibition of RMTg-VTA GABAergic pathway restores sucrose consumption in CFA treated animals. (open bars-baseline, filled bars – 48 hours (CNO) and 72 hours (VEH) post CFA). two-way ANOVA for repeated measures, time: F2, 40=28.60, p<0.0001; interaction (time × treatment): F4,40=6.707, p=0.0003; Sidak’s post hoc within group: hM3Di + CFA baseline(n=8) versus hM3Di + CFA + VEH (n=8), **** p<0.0001; hM3Di + CFA + CNO(n=8) versus hM3Di + CFA + VEH (n=8), *** p=0.0002; m-Cherry + CFA baseline(n=8) versus m-Cherry + CFA + CNO(n=8) ), **** p<0.0001; m-Cherry + CFA baseline(n=8) versus m-Cherry + CFA + VEH(n=8) ), **** p<0.0001). k. Inhibition of RMTg-VTA GABAergic pathway does not alter CFA induced hyperalgesia. (two-way ANOVA for repeated measures, time: F2, 40 = 53.58, p<0.0001; interaction (time × treatment): F4, 40 = 13.19, p<0.0001; Sidak’s post hoc for each group as compared to the group’s baseline session: **** p<0.0001). The data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m.
