Figure 4. Knockdown of IL-1 receptor type I (IL-1R1) expression in the DRN facilitated aggressive behavior of male mice.
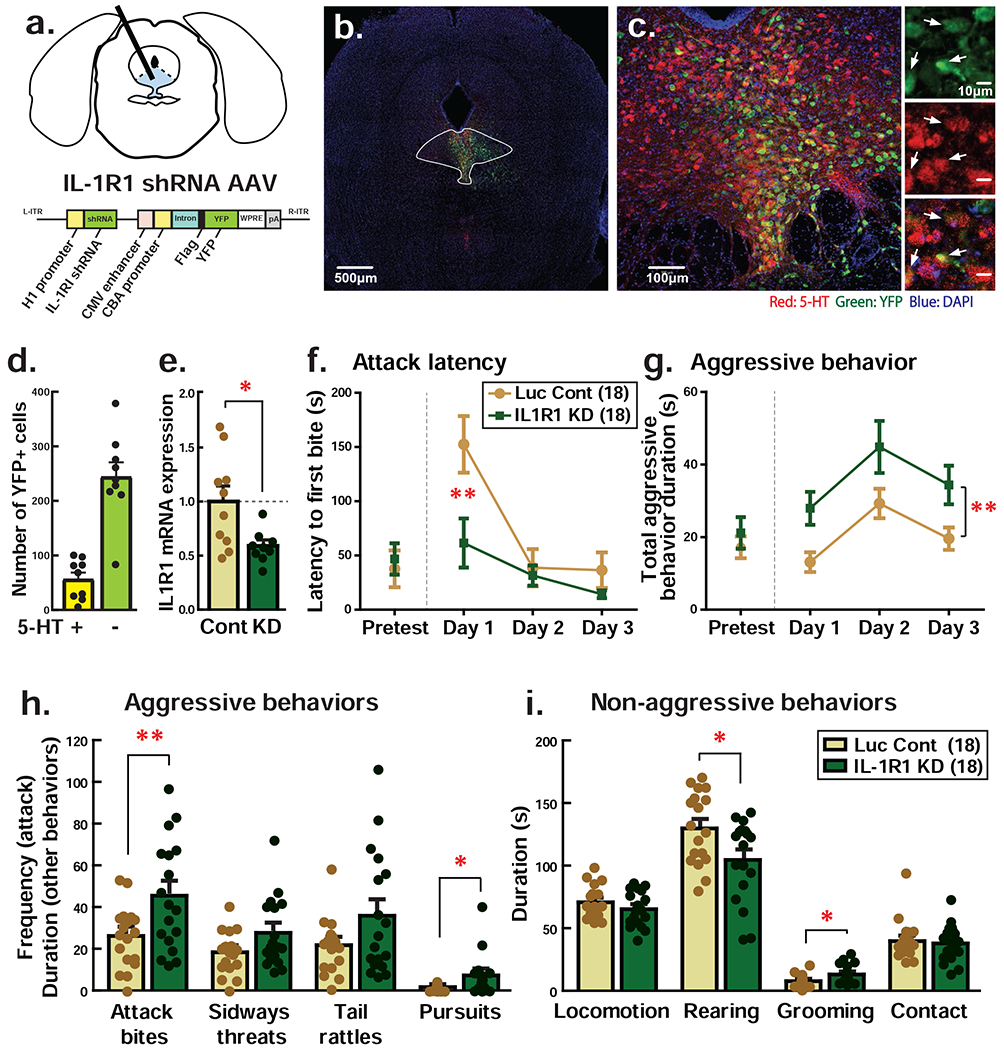
a Schematics of IL-1R1 knockdown (KD) in the DRN and IL-1R1 shRNA expressing AAV construct. IL-1R1 shRNA AAV also expresses YFP as a marker under the different promoter. b-c Representative pictures of IL-1R1 shRNA AAV infection in the DRN. Green: YFP, Red: serotonin (5-HT), Blue: DAPI. Inserted pictures in the right side of c showed enlarged pictures of YFP-positive cells (top), 5-HT-positive cells (middle) and their co-localization in the merged picture (bottom). White arrows indicate YFP-positive 5-HT neurons. d Number of YFP-positive cells on 5-HT-immunopositive neurons (5-HT+) and non-serotonergic neurons (5-HT−). e Quantitative PCR expression analysis of IL-1R1 mRNA in the DRN. Cont: Luciferase (Luc) shRNA expressing AAV injection control, KD: IL-1R1 shRNA expressing AAV injection into the DRN. f-g Effect of IL-1R1 KD in the DRN on the attack latency (f) and duration of aggressive behaviors (g). h-i Detailed behavioral analysis for aggressive behaviors (h) and non-aggressive behaviors (i). Average data of 3-days resident intruder test was presented. Numbers in the parenthesis indicate the number of animals used in each group. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
