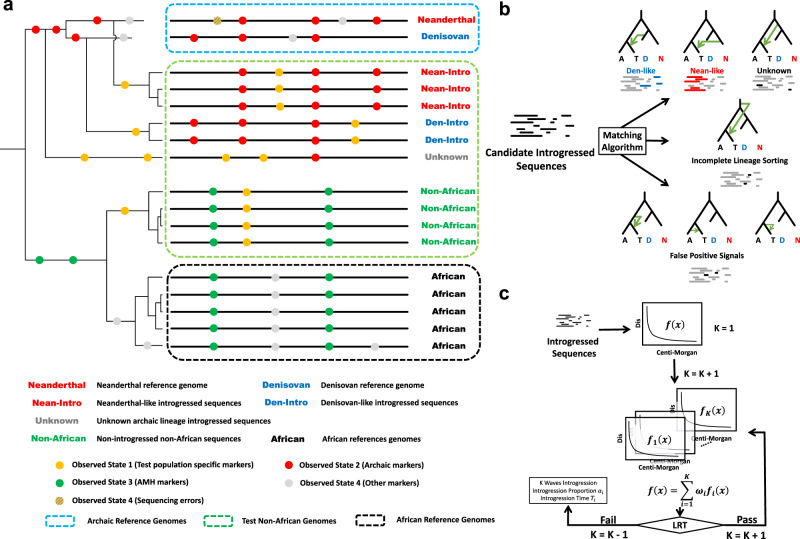
Fig. 1. ArchaicSeeker 2.0 schematic.
a Seeking algorithm. The light blue dashed box includes archaic reference genomes, the light green dashed box includes tested non-African human genomes, and the black dashed box includes African reference genomes. Dots in different colors stand for mutations of four different observation states in the HMM. b Matching algorithm. After we got the candidate introgressed sequences, we matched them to the seven topologies and found the best-matched one. Each topology corresponds to introgression for one specific lineage, incomplete lineage sorting, or a false-positive signal. c Reconstructing introgression history. For those introgressed sequences from one specific lineage, the length distribution was used to reconstruct the introgression history. A likelihood ratio test was used to find the most likely number of introgression events (K) and the software estimated introgression time and the proportion of each introgression event. AMH, anatomically modern human.