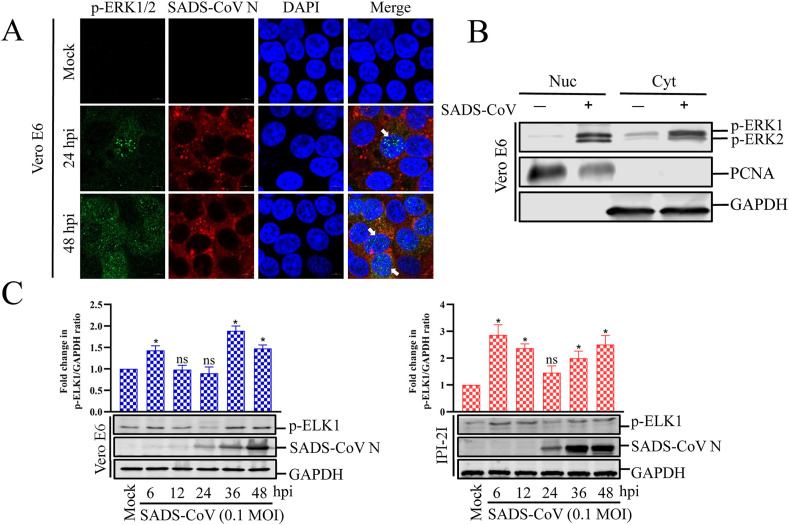
Fig. 2.
SADS-CoV induces nuclear translocation of active ERK1/2 and phosphorylates ELK1. (A) SADS-CoV induces nuclear translocation of p-ERK1/2. Vero E6 cells were mock infected or infected with SADS-CoV at MOI = 0.1 at different times. Cells were fixed and costained with antibodies directed against p-ERK1/2 (green) and SADS-CoV N (red). The cells were then counterstained with DAPI and examined with a confocal laser scanning microscope (Zeiss). (B) Representative western blot of cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts of Vero E6 cells mock treated or infected with SADS-CoV for 36 h. GAPDH and PCNA reflect cytoplasmic and nuclear contents, respectively. (C) SADS-CoV induces ELK1 phosphorylation. Vero E6 and IPI-2I cells were mock infected or infected with SADS-CoV at MOI = 0.1 at different times. Western blotting analysis with antibody specific for phosphorylated ELK1 (p-ELK1) or SADS-CoV N protein. GAPDH was used as the internal loading control. Fold changes in the (p-ELK1)/(GAPDH) ratio are plotted. Results are representative means of three independent experiments, and error bars denote SD. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)