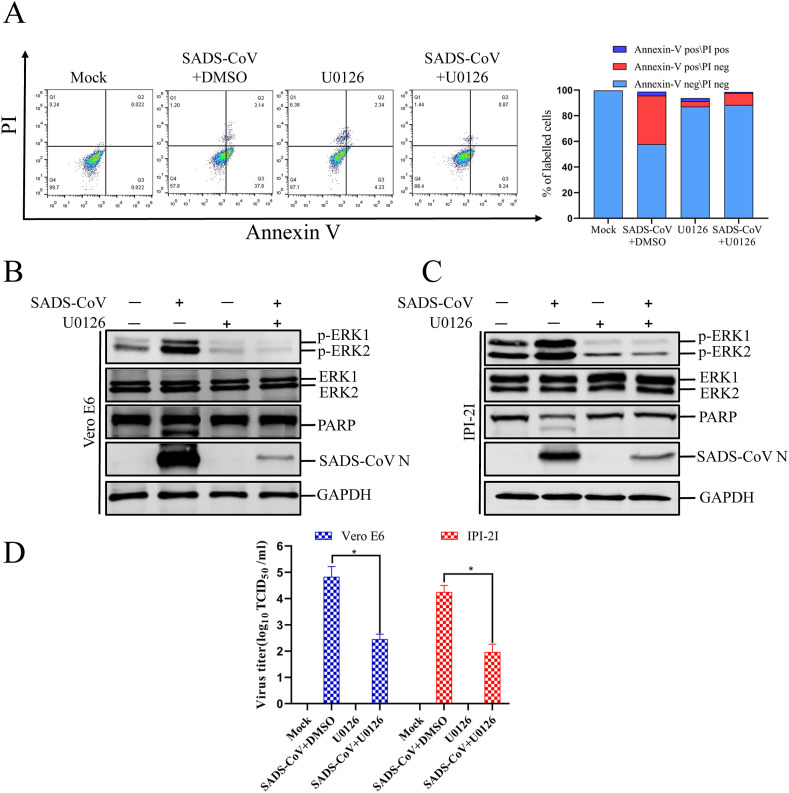
Fig. 5.
U0126 blocks SADS-CoV-induced apoptosis. (A) Vero E6 cells were mock infected or infected with SADS-CoV (MOI = 0.1) in the presence or absence of U0126 (10 μM) for 36 h. They were washed twice with cold PBS and resuspended in 1 × binding buffer. The cells were stained with FITC–annexin V and PI for 15 min and analyzed with flow cytometry (BD FACSCalibur, USA) within 1 h. Q1: necrotic or other cell population, which was FITC–annexin V negative and PI positive; Q2: end-stage apoptotic or dead cell population, which was FITC–annexin V and PI positive; Q3: early apoptotic cell population, which was FITC–annexin V positive and PI negative; Q4: viable cell population that was not undergoing apoptosis, which was both FITC–annexin V and PI negative. The graph on the right represents the percentage of each cell population nonsignificant percentages of annexin-V-negative and PI-positive cells were excluded. (B and C) Vero E6 and IPI-2I cells were mock infected or infected with SADS-CoV at an MOI of 0.1 in the presence or absence of U0126 (10 μM). After incubation for 36 h, a western blotting analysis with antibody specific for p-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, PARP, or SADS-CoV N protein. GAPDH was used as the internal loading control. (D) The virus-containing supernatants were collected at 36 hpi and the viral titers were calculated with the Spearman–Kärber method. Error bars represent the standard errors of the means of three independent experiments.