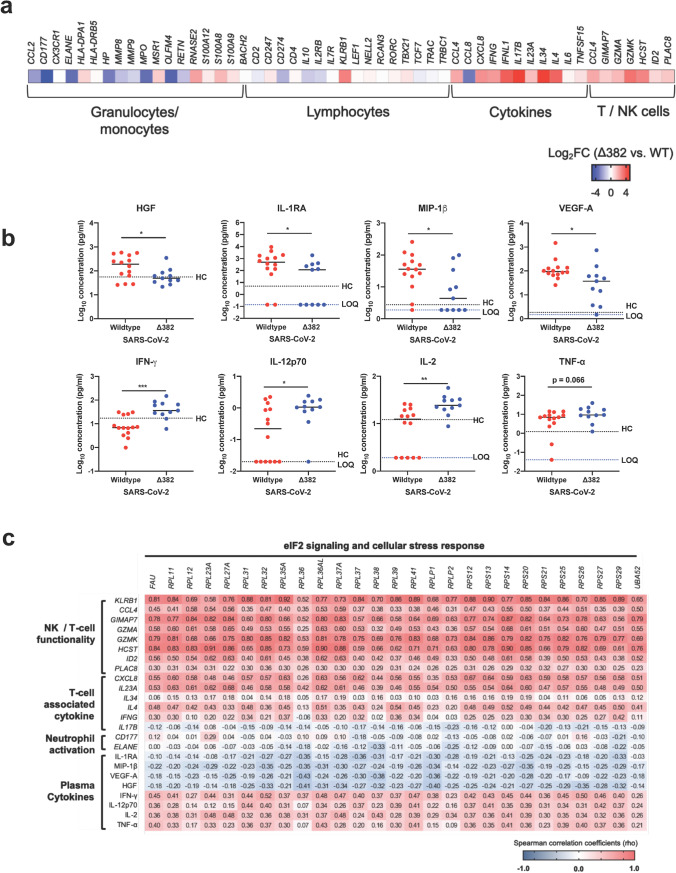
Fig. 3.
Effects of 382-nt deletion in SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 genome on immune responses in COVID-19 patients. Transcriptomic and cytokine profiles of COVID-19 patients infected with WT (n = 14) or Δ382 SARS-CoV-2 (n = 11) at the acute phase of infection (SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive; median 8 days PIO) were analyzed. a Expressions of genes associated with granulocytes, monocytes, lymphocytes, cytokines and T/NK cell functionality were compared between COVID-19 patients infected with WT or Δ382 SARS-CoV-2. Heatmaps of the DEGs, scaled based on log2FC values, with blue and red colors indicating low and high expressions, respectively. b Plasma immune mediator levels of COVID-19 patients infected with WT (n = 14) or Δ382 SARS-CoV-2 (n = 11) at the acute phase of infection (SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive; median 8 days PIO) and profiles of significant immune mediators are illustrated as scatter plots and shown as mean. Mann–Whitney U tests were conducted on the logarithmically transformed concentration values (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). Respective mean concentrations of immune mediators from healthy controls (HC; n = 23) are indicated as black dotted lines. Patient samples with concentrations out of measurement range are presented as the logarithmically transformed value of LOQ and indicated as blue dotted lines. c Association between elF2 signaling and immune signatures in Δ382 SARS-CoV-2 infection. Spearman’s correlation matrix for the genes associated with eIF2 signaling, T cell functionality, neutrophil activation and plasma cytokines. Colors represent the Spearman correlation coefficients (rho) between the expression of genes related to eIF2 signaling and genes or immune mediators associated with different immune phenotypes. FC, fold change, WT, wildtype; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PIO, post-illness onset; DEGs, differentially expressed genes; LOQ, limit of quantification