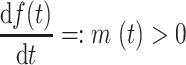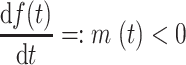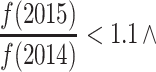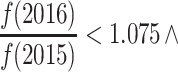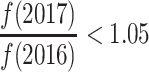Table 2.
Types of adoption curves and associated technologies
| Type | Criterion | Technologies (no.) |
|---|---|---|
| (I) Continuous increase |
∀ t ∈ [2006; 2017] |
HCI, MR-PTC, S-ICD, IAHEI, SCO-MAGN, BS-PV, SE-DES, TAVI, BS-VSAV, DCB-SUAV, DCB-LAV, DCB-AV, SCB-ULV, DCB-LLV, DCB-ARTV (n = 15) |
| (II) Continuous decrease |
∀ t ∈ [2006; 2017] |
SE-BMS (n = 1) |
| (III) Reaching a saturation |
f(2015) > f(t) ∀ t < 2015 |
EL-P/ICD, MRD, DCB-CV (n = 3) |
| (IV) “Local maximum”: Continuous increase followed by continuous decrease |
m(tI) > 0 ∧ m(tII) < 0 tI ∈ [ti; tj], tII ∈ [tj; tk] ti, tj < tk |
FE-AAA, ACT, ACCS, DEB-TACE, LVRC, BVS, BRA, IABC, MVR, FD-IV (n = 10) |
| (V) “Local minimum”: Continuous decrease followed by continuous increase |
m(tI) < 0 ∧ m(tII) > 0 tI ∈ [ti; tj], tII ∈ [tj; tk] ti, tj < tk |
MVAC, FD-ULV (n = 2) |
| (VI) Complex | NA | |
| (VI.a) | According to hierarchical-agglomerative clustering method (see Additional file 2) | PECLA/iLA, pVAD, EVCT, CBS, ACD, VEPTR, IAELC, UD-DJMS, DES-LLV, EABO, HCO, IAVC, SP-ENDOST, FDT, DES-SAA, MESI, EBV, NEURO, IABC-EL, DES-ULV, PVR, DCB-TV, DCB-OTHV (n = 23) |
| (VI.b) | According to hierarchical-agglomerative clustering method (see Additional file 2) | IET-MICRO, F-TUR, DCB-IV, DCB-VV, ER-ABL (n = 5) |