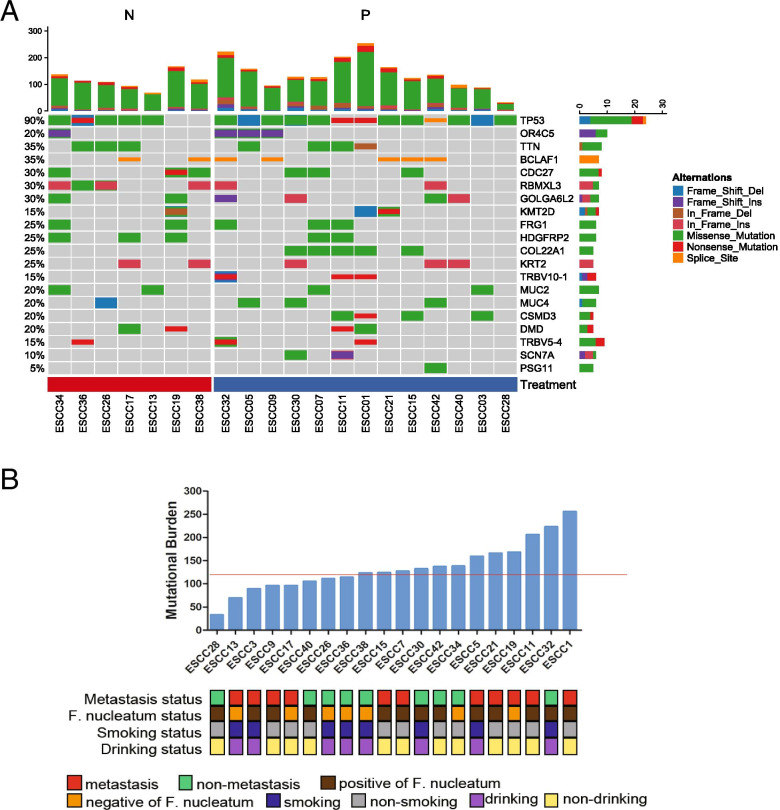
Fig. 7.
(A) Mutation frequencies and signatures, and significantly mutated genes in 20 ESCCs. The number of somatic mutations of each examined case (top) and the significantly mutated genes (SMGs) colored by the types of mutations and their mutational frequency (bottom). Columns, examined cases; rows, genes; N, F. nucleatum-negative group; P, F. nucleatum-positive group. (B) Combination of the mutational burden and the F. nucleatum content to predict metastasis in ESCC. The red horizontal line indicates the cutoff score for mutational burden. Clinical and pathological features that include the presence or absence of distant metastases in the surgical specimen are annotated for each patient. A sample was considered F. nucleatum positive if the qPCR Ct value was < 37 and the melt curve could be generated; otherwise, it was considered negative