Fig. 4.
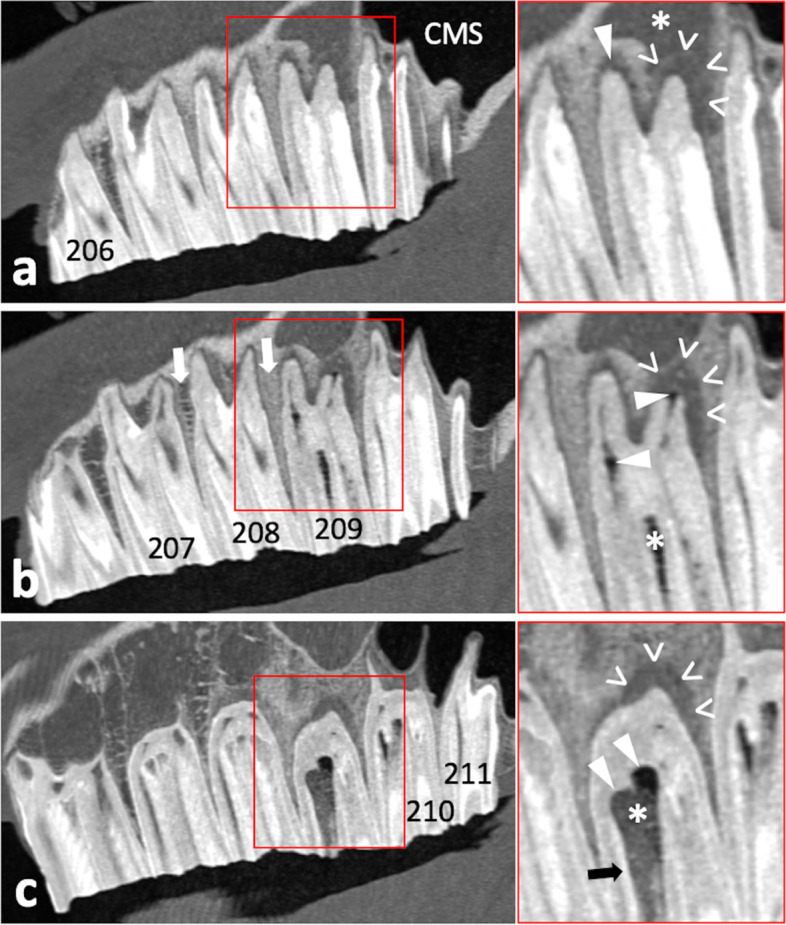
Sagittal CT image sections of left maxillary cheek teeth and adjacent sinusoidal structures. a – c Section plane moving from buccal to medial; 0.6 mm slice thickness; W3100/C500. a Osteolytic loss of sinusoidal lamina dura of the buccodistal root of 209 (open arrowheads) and resulting apicosinusoidal fistulation with rostral maxillary sinus showing soft tissue/ fluid dense filling (asterisk). Normal pneumatized caudal maxillary sinus (CMS). Widening of periodontal space buccomesial root of 209 (arrowhead). b Gas inclusions in the buccomesial pulp and apical end of the buccodistal pulp (arrowheads). The periodontium at the buccodistal root of 209 shows severe periapical bone loss and inflammatory enlargement of periodontal space (open arrowheads). Slight central infundibular cement loss of the mesial infundibulum 209 (asterisk). Normal trabecular appearance of interalveolar bone between 207/208 and sclerosis between 208/209 (arrows). c Subocclusally, the severely enlarged mesial infundibulum of 209 shows missing infundibular cement (hypoplasia) and filling with heterogenic hypodense material and gas (asterisk). Missing enamel lining of the infundibular fundus (arrowheads), while e.g. parietal infundibular enamel is still present (arrow). Severe periapical bone loss and enlargement of the periodontal space (open arrowheads)
