Figure 2.
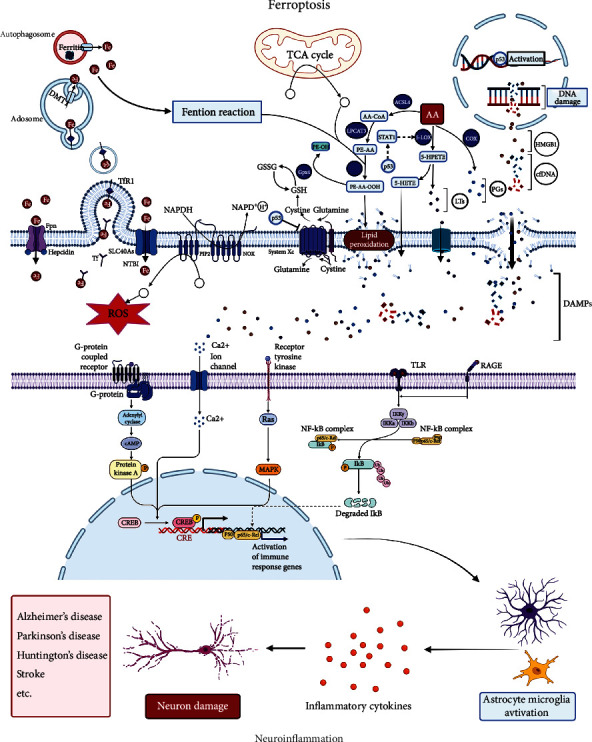
Putative pathway for ferroptosis participates in neuroinflammation to neurological disorders. Damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecules (e.g., ROS, cfDNA, HMGB1, ITs, and PGs) produced in the process of ferroptosis activate glial cells by activating neuroimmune pathways. Activated glial cells produce a series of inflammatory factors which contribute to neuronal damage and a series of neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, and stroke.
