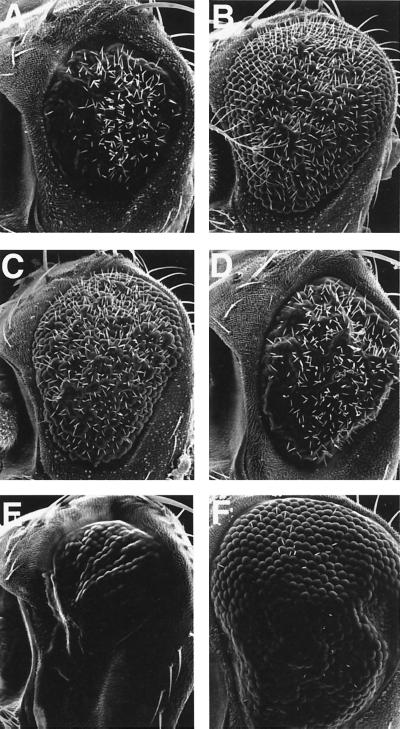
FIG. 5.
Genetic interaction of pGMR-mTAK1ΔN. (A to F) Scanning electron micrographs of the compound eye. (A) GMR-GAL4/UAS-dTAK1(weak); (B) hep1/Y; GMR-GAL4/UAS-dTAK1(weak); (C) GMR-GAL4/UAS-dTAK1(weak); bsk2/+; (D) Dsor1LH110/Y; GMR-GAL4/UAS-dTAK1(weak) (E) GMR-GAL4/+; UAS-hep/+; (F) GMR-GAL4/+; UAS-hep/pGMR-p35. Reduced eye phenotype of GMR-GAL4/UAS-dTAK1 (A) is suppressed by one copy reduction of the hep or bsk gene (B and C). In contrast to this, a mutant which is involved in MAPK/ERK cascade, Dsor1, does not show any genetic interaction to this phenotype (D). Ectopic expression of hep also results in the small eye phenotype (E). This phenotype is suppressed by the presence of p35 (F), indicating that ectopic activation of the JNK signal induced apoptosis in the developing eye. GMR-GAL4/UAS-hep flies lost most of the interommatidial bristles (E). Bristle phenotype is not rescued by p35 expression (F), suggesting that apoptosis is not a direct cause of this phenotype. Anterior is to the left, and dorsal is up.