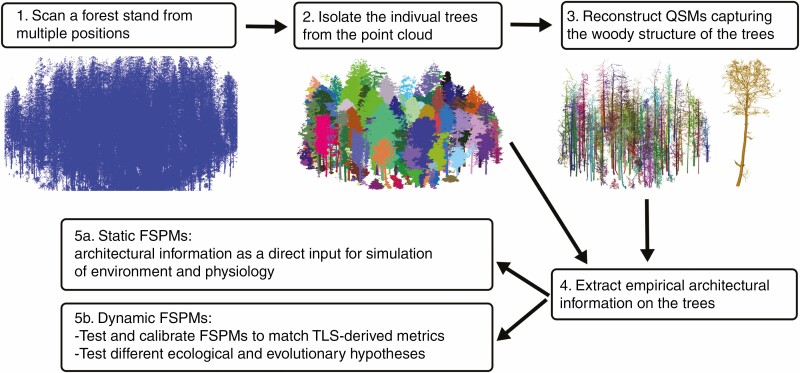
Fig. 6.
A potential TLS to FSPM workflow. 1. To minimise occlusion and gain an even point coverage, individuals should be scanned from multiple positions at regular intervals (see Wilkes et al. 2017). 2. Trees can be segmented from the large scan using segmentation software, LidR (Roussel et al. 2020) treeseg (Burt et al. 2018) or 3DForest (Trochta et al., 2017). 3. Generate QSMs for each individual in the scan (Raumonen et al. 2013) 4. Extract the appropriate structural information for use in FSPMs. 5a. Structural information can be used directly to simulate function with static woody structure and changing environmental conditions. 5B. Alternatively, structural information can be used to initialise FSPMs, aid validation and calibrate dynamic models with changes in woody structure.