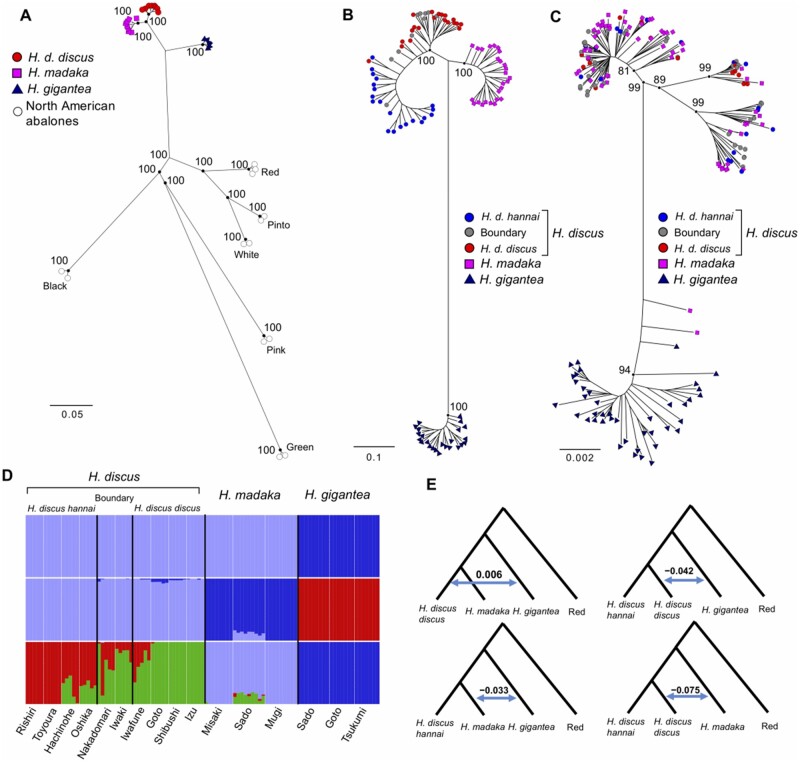
Fig. 2.
(A) ML tree of the Western Pacific and the North American abalones (Red: Haliotis rufescens, Pinto: H. kamtschatkana, White: H. sorenseni. Black: H. cracherodii, Pink: H. corrugate, Green: H. fulgens) based on whole-genome sequencing data (46,366 SNP loci). (B) ML tree of the Western Pacific abalones based on GRAS-Di data (18,109 SNP loci). (C) Neighbor-joining tree based on the mitochondrial genomes of the Western Pacific abalones. The values in the nodes in (A)–(C) are bootstrap values. (D) Individual admixture proportions (q-values) among the Western Pacific abalones estimated by ADMIXTURE. (E) D-statistics of the Western Pacific abalones (z-score [D-statistic/standard error] > 3). The Red abalone (H. rufescens) was used as an outgroup in calculation of D-statistics.