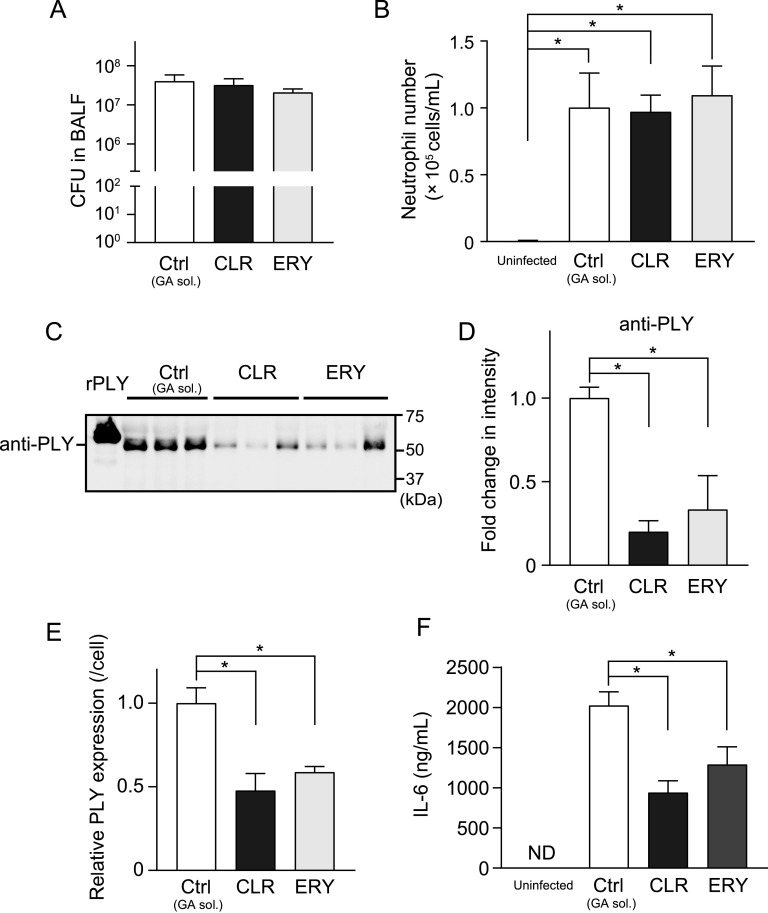
FIG 5.
Administration of CLR or ERY decreased the PLY protein level without affecting pneumococcal CFU and neutrophil infiltration in BALF. BALB/c mice (eight mice in each group) were intratracheally infected with MRSP NU4471 (5 × 108 CFU in 50 μl PBS). Uninfected mice were intratracheally administered 50 μl PBS only. CLR (150 mg/kg), ERY (150 mg/kg), or gum arabic solution (GA sol.; Ctrl) was administered orally to the infected mice every 12 h. The animals were sacrificed at 24 h postinfection. (A) BALF samples were plated onto blood agar plates and cultured aerobically to enumerate the number of recovered pneumococci. (B) The number of neutrophils was determined by flow cytometry based on the expression of both Ly6G and CD11b. (C) PLY protein levels in the BALF were determined by Western blotting. A representative Western blot image (three samples from each group) is shown. (D) Relative intensities of the bands were quantitatively analyzed. (E) Relative intensities of the bands were normalized to viable pneumococcal cell numbers in BALF. (F) IL-6 levels in BALF were determined using ELISA kits. In panels A, B, and D to F, the data represent the mean ± SEM and were evaluated using one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. *, Significant difference between the indicated groups at P < 0.05. BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; CLR, clarithromycin; Ctrl, control; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ERY, erythromycin; GA sol., gum arabic solution; IL, interleukin; MRSP, macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae; ND, not detected; rPLY, recombinant pneumolysin; SEM, standard error of the mean.