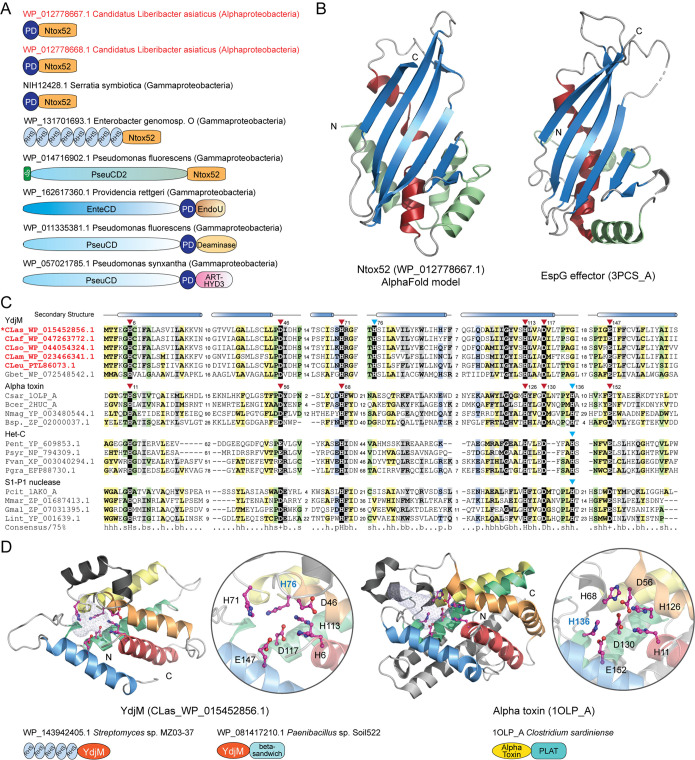
FIG 7.
Identification of potential protein toxins. (A) Domain architectures of representative polymorphic toxins containing the PD domain and the Ntox52 domain. The PD toxins of “Ca. Liberibacter asiaticus” are highlighted in red. Domain architectures are labeled by accession numbers, species names, and their lineages in parentheses. Domain architectures are not drawn to scale. (B) The AlphaFold2 model of Ntox52 and its structural similarity with the EspG effector (PDB: 3PCS_A). (C) Multiple sequence alignment between the YdjM, alpha toxin, Het-C, and S1-P1 nuclease domains. The conserved catalytic residues are highlighted with a black background. (D) Structural comparison of YdjM and the alpha toxin domains. Representative domain architectures of these toxin proteins are shown.